Discussion
Home ‣ Chemical Engineering ‣ Fertiliser Technology See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Raw materials for urea production are
Options- A. CO2 and N2
- B. CO2, H2 and N2
- C. NH3 and CO
- D. HNO3 and CaCO3
- Correct Answer
- CO2, H2 and N2
- 1. Cellulose content in bomboo fibre is about __________ percent.
Options- A. 10
- B. 20
- C. 50
- D. 85 Discuss
- 2. Gold ore concentration is mostly done using
Options- A. jigging
- B. tabling
- C. froth floatation
- D. elutriation Discuss
- 3. Vapor pressure of water at 100°C is about __________ bar.
Options- A. 0.1013
- B. 1.013
- C. 10.13
- D. 101.3 Discuss
- 4. P2O5 content in triple superphosphate is about __________ percent.
Options- A. 42-50
- B. 15-20
- C. 85-90
- D. 70-75 Discuss
- 5. For a cylindrical shell, (subject to the thickness of uppermost course being more than the minimum for diaofthe tank in question), the thickness of the courses of shell
Options- A. decreases upwards.
- B. increases upwards.
- C. remains same throughout.
- D. may decrease or increase upwards depending upon whether vacuum or positive pressure would be maintained inside the shell. Discuss
- 6. Water is flowing through a series of four tanks and getting heated as shown in figure. It is desired to design a cascade control scheme for controlling the temperature of water leaving the tank 4 as there is a disturbance in the temperature of a second stream entering the tank 2. Select the best place to take the secondary measurement for the second loop.
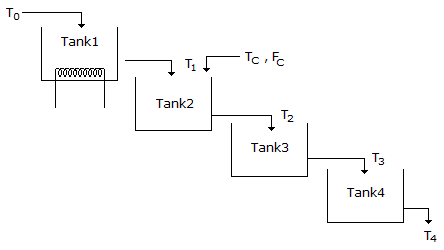
Options- A. Tank 1
- B. Tank 2
- C. Tank 3
- D. Tank 4 Discuss
- 7. The gas which contributes maximum to the heating value of natural gas is
Options- A. CO
- B. CO2
- C. H2
- D. CH4 Discuss
- 8. Pick out the wrong unit conversion.
Options- A. l kgf= 9.8 Newton.
- B. 1 stoke = 1 m2/second.
- C. 1 Pascal second = 10 poise.
- D. 1 ppm = 1 ml/m3 = 1 mg/kg. Discuss
- 9. Styrene butadiene rubber is commercially manufactured by
Options- A. bulk polymerisation
- B. suspension polymerisation
- C. solution polymerisation
- D. emulsion polymerisation Discuss
- 10. Fast breeder nuclear reactors using enriched uranium as fuel may contain upto a maximum of __________ percent of U-235 (i.e. fissile material).
Options- A. 15
- B. 45
- C. 65
- D. 85 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 50
Correct Answer: tabling
Correct Answer: 1.013
Correct Answer: 42-50
Correct Answer: decreases upwards.
Correct Answer: Tank 3
Correct Answer: CH4
Correct Answer: 1 stoke = 1 m2/second.
Correct Answer: emulsion polymerisation
Correct Answer: 85
Comments
There are no comments.More in Chemical Engineering:
Chemical Engineering BasicsChemical Engineering Plant EconomicsChemical Engineering ThermodynamicsChemical ProcessChemical Reaction EngineeringEnvironmental EngineeringFertiliser TechnologyFluid MechanicsFuels and CombustionFurnace TechnologyHeat TransferMass TransferMaterials and ConstructionMechanical OperationsNuclear Power EngineeringPetroleum Refinery EngineeringPolymer TechnologyProcess Control and InstrumentationProcess Equipment and Plant DesignRefractory TechnologyStoichiometryProgramming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
