Discussion
Home ‣ Mechanical Engineering ‣ Heat Transfer, Refrigeration and Air Conditioning See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
In air-conditioning of aeroplanes, using air as a refrigerant, the cycle used is
Options- A. reversed Carnot cycle
- B. reversed Joule cycle
- C. reversed Brayton cycle
- D. reversed Otto cycle
- Correct Answer
- reversed Brayton cycle
- 1. The function of an oil control orifice is that it
Options- A. returns cylinder head lubricating oil to the oil pan at high speed
- B. turns oil into fine mist for spray lubrication
- C. regulates the pressure of engine oil supplied by the oil pump for the lubrication of cylinder head mechanism and other purposes
- D. removes impurities from cylinder head lubricating oil Discuss
- 2. The missing quantity per stroke is equal to
Options- A. cylinder feed - indicated mass of steam
- B. cylinder feed + indicated mass of steam
- C. mass of cushion steam + indicated mass of steam
- D. mass of cushion steam + cylinder feed Discuss
- 3. Quenching is not necessary when hardening is done by
Options- A. case hardening
- B. flame hardening
- C. nitriding
- D. any one of these Discuss
- 4. The term 'force' may be defined as an agent which produces or tends to produce, destroys or tends to destroy motion.
Options- A. Agree
- B. Disagree Discuss
- 5. Nodular cast iron is produced by adding __________ to the molten cast iron.
Options- A. nickel
- B. chromium
- C. copper
- D. magnesium Discuss
- 6. Which of the following statement is correct as regard to centrifugal compressors?
Options- A. The flow of air is parallel to the axis of the compressor.
- B. The static pressure of air in the impeller increases in order to provide centripetal force on the air.
- C. The impeller rotates at high speeds.
- D. The maximum efficiency is higher than multi-stage axial flow compressors. Discuss
- 7. Parallel fillet welds are designed for bending strength.
Options- A. Agree
- B. Disagree Discuss
- 8. When the dimension is expressed as
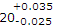 , then the basic size is
, then the basic size is
Options- A. 20 mm
- B. 20.035 mm
- C. 20.025 mm
- D. 19.975 mm Discuss
- 9. The temperature required for full annealing in hyper-eutectoid steel is
Options- A. 30° C to 50° C above upper critical temperature
- B. 30° C to 50° C below upper critical temperature
- C. 30° C to 50° C above lower critical temperature
- D. 30° C to 50° C below lower critical temperature Discuss
- 10. The wet bulb depression is zero when relative humidity is
Options- A. zero
- B. 0.5
- C. 0.75
- D. 1.0 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: regulates the pressure of engine oil supplied by the oil pump for the lubrication of cylinder head mechanism and other purposes
Correct Answer: cylinder feed - indicated mass of steam
Correct Answer: nitriding
Correct Answer: Agree
Correct Answer: magnesium
Correct Answer: The static pressure of air in the impeller increases in order to provide centripetal force on the air.
Correct Answer: Agree
Correct Answer: 20 mm
Correct Answer: 30° C to 50° C above lower critical temperature
Correct Answer: 1.0
Comments
There are no comments.More in Mechanical Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
