Discussion
Home ‣ Mechanical Engineering ‣ Thermodynamics See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
When a gas is heated at constant pressure
Options- A. its temperature will increase
- B. its volume will increase
- C. both temperature and volume will increase
- D. neither temperature not volume will increase
- Correct Answer
- both temperature and volume will increase
- 1. A flow in which each liquid particle has a definite path, and the paths of individual particles do not cross each other, is called
Options- A. steady flow
- B. uniform flow
- C. streamline flow
- D. turbulent flow Discuss
- 2. A simply supported beam 'A' of length l, breadth b and depth d carries a central point load W. Another bream 'B' has the same length and breadth but its depth is doubled. The deflection of beam 'B' will be double as compared to beam 'A'.
Options- A. Correct
- B. Incorrect Discuss
- 3. The ability of a material to undergo large permanent deformation with the application of a tensile force, is called ductility.
Options- A. Correct
- B. Incorrect Discuss
- 4. The injector nozzle of a compression ignition engine is required to inject fuel at a sufficiently high pressure in order to
Options- A. inject fuel in a chamber of high pressure at the end of compression stroke
- B. inject fuel at a high velocity to facilitate atomisation
- C. ensure that penetration is not high
- D. all of the above Discuss
- 5. The energy possessed by a body, for doing work by virtue of its position, is called
Options- A. potential energy
- B. kinetic energy
- C. electrical energy
- D. chemical energy Discuss
- 6. The average time recorded by work study man for an operation is called
Options- A. standard time
- B. normal time
- C. representative time
- D. none of these Discuss
- 7. The material of pipe lines for a system using freon as a refrigerant should be
Options- A. brass
- B. copper
- C. steel
- D. aluminium Discuss
- 8. Manganese bronze has
Options- A. good wearing qualities and high elasticity
- B. high yield point, high fatigue limit and excellent cold and hot corrosion resistance
- C. high resistance to corrosion
- D. valuable cold working property Discuss
- 9. The frequency of oscillation of a compound pendulum is(where kG = Radius of gyration about the centroidal axis, and h = Distance between the point of suspension and C.G. of the body.)
Options- A.
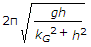
- B.
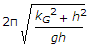
- C.
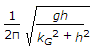
- D.
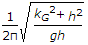 Discuss
Discuss
- 10. Frequency of vibrations means the number of cycles per second.
Options- A. Yes
- B. No Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: streamline flow
Correct Answer: Incorrect
Correct Answer: Correct
Correct Answer: all of the above
Correct Answer: potential energy
Correct Answer: representative time
Correct Answer: copper
Correct Answer: high resistance to corrosion
Correct Answer:
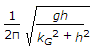
Correct Answer: Yes
Comments
There are no comments.More in Mechanical Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
