Discussion
Home ‣ Mechanical Engineering ‣ Engineering Mechanics See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Moment of inertia of a rectangular section having width (b) and depth (d) about an axis passing through its C.G. and parallel to the width (b), is
Options- A.
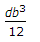
- B.
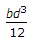
- C.
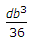
- D.
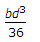
- Correct Answer
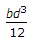
- 1. The injection pressure in a diesel engine is about
Options- A. 10 bar
- B. 100 bar
- C. 150 bar
- D. 500 bar Discuss
- 2. The discharge is __________ at critical pressure.
Options- A. zero
- B. minimum
- C. maximum Discuss
- 3. The heating and expanding of a gas is called thermodynamic system.
Options- A. Yes
- B. No Discuss
- 4. The workdone in a free expansion process is zero.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 5. The rivets are used for __________ fastenings.
Options- A. permanent
- B. temporary Discuss
- 6. The limit of eccentricity is based upon no tension condition.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 7. A file with 50 - 60 teeth in 25 mm is called bastard file.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 8. Blast furnace is used to produce
Options- A. pig iron
- B. cast iron
- C. wrought iron
- D. steel Discuss
- 9. In welding aluminium with TIG arc welding, alternating current is used.
Options- A. Correct
- B. Incorrect Discuss
- 10. German silver contains
Options- A. 1% silver
- B. 2% silver
- C. 5% silver
- D. no silver Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 100 bar
Correct Answer: maximum
Correct Answer: No
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: permanent
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: pig iron
Correct Answer: Correct
Correct Answer: no silver
Comments
There are no comments.More in Mechanical Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
