Discussion
Home ‣ Chemical Engineering ‣ Fuels and Combustion See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Temperature of preheated air used for the transportation of pulverised coal through pipes to the burner of a boiler furnace is restricted to a maximum limit of about 300° C to avoid the
Options- A. requirement of large volume combustion chamber.
- B. risk of explosion.
- C. chances of clinker formation.
- D. incomplete combustion of coal.
- Correct Answer
- risk of explosion.
- 1. Unit of mass velocity is
Options- A. kg/m . hr
- B. kg/m2.hr
- C. kg/hr
- D. kg/m2 Discuss
- 2. As per Kirchoff s equation, the heat of reaction is affected by the
Options- A. pressure
- B. volume
- C. temperature
- D. molecularity Discuss
- 3. Which of the following is not a component of the fixed capital for a chemical plant facility?
Options- A. Raw materials inventory.
- B. Utilities plants.
- C. Process equipment.
- D. Emergency facilities. Discuss
- 4. Dust laden air can be purified using a
Options- A. cyclone separator
- B. bag filter
- C. gravity settler
- D. tubular centrifuge Discuss
- 5. Nylon-66 compared to nylon-6 has
Options- A. lower melting point.
- B. more abrasion resistant properties.
- C. higher hardness.
- D. all (a), (b) and (c). Discuss
- 6. The transfer function for a PID controller is (where, ? i is the integral (reset) time and ?D is the derivative time.)
Options- A. Kc(1 + ?is + ?D ). s
- B.
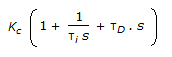
- C.
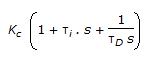
- D.
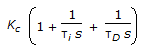 Discuss
Discuss
- 7. Shock resisting steels should possess high
Options- A. hardness
- B. toughness
- C. tensile strength
- D. wear resistance Discuss
- 8. The optimum moisture content in solids to be crushed/ground ranges from __________ percent.
Options- A. 3 to 4
- B. 8 to 10
- C. 10 to 15
- D. 15 to 20 Discuss
- 9. If a single tube pass heat exchanger is converted to two passes; for the same flow rate, the pressure drop per unit length in tube side will __________ times.
Options- A. increase by 1.8
- B. decrease by 22
- C. increase by 21.6
- D. none of these Discuss
- 10. For a given mass of a gas at constant temperature, if the volume 'V' becomes three times, then the pressure 'P' will become
Options- A. P/3
- B. 3P
- C. 9P2
- D. 9P Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: kg/m2.hr
Correct Answer: temperature
Correct Answer: Raw materials inventory.
Correct Answer: cyclone separator
Correct Answer: higher hardness.
Correct Answer:
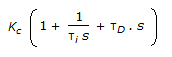
Correct Answer: toughness
Correct Answer: 3 to 4
Correct Answer: increase by 21.6
Correct Answer: P/3
Comments
There are no comments.More in Chemical Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
