Discussion
Home ‣ Mechanical Engineering ‣ Steam Nozzles and Turbines See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The rate of discharge through the nozzle __________ when the exit pressure is gradually reduced.
Options- A. remains same
- B. decreases
- C. increases
- Correct Answer
- increases
- 1. The maximum bending moment of a cantilever beam of length l and carrying a uniformly distributed load of w per unit length lies at the middle of its length.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 2. The tool life in case of a grinding wheel is the time
Options- A. between two successive regrinds of the wheel
- B. taken for the wheel to be balanced
- C. taken between two successive wheel dressings
- D. taken for a wear of 1 mm on its diameter Discuss
- 3. When there is no increase or decrease in shear force between two points, it indicates that there is no change in the bending moment between these points.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 4. When a body is subjected to a direct tensile stress (?x) in one plane accompanied by a simple shear stress (?xy), the maximum shear stress is
Options- A.
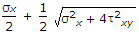
- B.
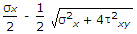
- C.
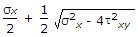
- D.
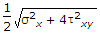 Discuss
Discuss
- 5. The floating position of the holding fixture in a rotary transfer device is used to
Options- A. improve the accuracy of location
- B. reduce the tendency to over-index
- C. improve upon the acceleration and deceleration characteristics
- D. reduce the cycle time Discuss
- 6. Coefficient of velocity is defined as the ratio of
Options- A. actual velocity of jet at vena contracta to the theoretical velocity
- B. area of jet at vena contracta to the area of orifice
- C. actual discharge through an orifice to the theoretical discharge
- D. none of the above Discuss
- 7. The unit of dynamic viscosity in S.I. units is
Options- A. N-m/s2
- B. N-s/m2
- C. poise
- D. stoke Discuss
- 8. In a four stroke cycle diesel engine, the inlet valve
Options- A. opens at 20° before top dead centre and closes at 40° after bottom dead centre
- B. opens at 20° after top dead centre and closes at 20° before bottom dead centre
- C. opens at top dead centre and closes at bottom dead centre
- D. may open and close anywhere Discuss
- 9. The coefficient of performance of electrolux refrigerator is the ratio of
Options- A. heat supplied by the gas burner to the heat absorbed by the evaporator
- B. heat absorbed by the evaporator to the heat supplied by the gas burner
- C. heat supplied by the gas burner minus the heat absorbed by the evaporator to the heat supplied by the gas burner
- D. heat absorbed by the evaporator minus the heat supplied by the gas burner to the heat absorbed by the evaporator Discuss
- 10. Silicon is added in low carbon steels to
Options- A. make the steel tougher and harder
- B. make the steel of good bending qualities
- C. raise the yield point
- D. all of these Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: taken between two successive wheel dressings
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer:
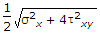
Correct Answer: reduce the cycle time
Correct Answer: actual velocity of jet at vena contracta to the theoretical velocity
Correct Answer: N-s/m2
Correct Answer: opens at 20° before top dead centre and closes at 40° after bottom dead centre
Correct Answer: heat absorbed by the evaporator to the heat supplied by the gas burner
Correct Answer: make the steel tougher and harder
Comments
There are no comments.More in Mechanical Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
