Discussion
Home ‣ Verbal Reasoning ‣ Syllogism See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
- Statements:
All carts are cars.
All cars are trains. So
Conclusions:
I. All carts are trains.
II. All trains are carts.
Options- A. Only conclusion I follows
- B. Only conclusion II follows
- C. Both conclusions I and II follow
- D. Neither conclusion I nor conclusion II follows
- Correct Answer
- Only conclusion I follows
ExplanationBoth the Premises are Universal Affirmative (A?type).
All carts are cars. ? All cars are trains.
A + A ? A-type of Conclusion
"All carts are trains."
This is Conclusion I. - 1. c _ bba _ cab _ ac _ ab _ ac
Options- A. abcbc
- B. acbcb
- C. babcc
- D. bcacb Discuss
- 2. NA
Options- A. 14th November
- B. 15th August
- C. 26th January
- D. 2nd October Discuss
- 3. Nebulous : Form
Options- A. Insincere : Misanthrope
- B. Benevolent : Excellence
- C. Insipid : Taste
- D. Composed : Innocence Discuss
- 4. 3 : 12 :: 5 :?
Options- A. 25
- B. 35
- C. 30
- D. 15 Discuss
- 5. Paper : Tree :: Glass :?
Options- A. Window
- B. Sand
- C. Stone
- D. Mirror Discuss
- 6. Statement:
Poverty persists under conditions where human resource is undervalued, and land and other material resources are overvalued.
Assumptions:
I. Poverty can be eradicated by enhancing the human resource value.
II. There should be a balance between the valuation of human and material resources.
Options- A. if only assumption I is implicit.
- B. if only assumption II is implicit.
- C. if either I or II is implicit.
- D. if neither I nor II is implicit. Discuss
- 7. 'Tall' is related to 'Dwarf' in the same way as 'Kind' is related to
Options- A. Weak
- B. Gentle
- C. Cruel
- D. Forgive Discuss
- 8. Truthfulness : Liar : : Loyalty :?
Options- A. Worker
- B. Traitor
- C. Diligent
- D. Faithful Discuss
- 9. Statements:
H * T, T S B, B © R
Conclusions:
I. R © H II. B © H III. T % R
Options- A. Only i is true
- B. Only I and II are true
- C. Only I and III are true
- D. Only II and III are true Discuss
- 10. _OPQ, N_PQ, NO_Q, NOP_
Options- A. ONQP
- B. NOQP
- C. NOPQ
- D. PQNO Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: acbcb
Explanation:
The given series is in the below pattern , we can see that
cabbac / cabbac / cabbac.
Hence , required answer will be acbcb .
Correct Answer: 14th November
Explanation:
All others are national holidays.
Correct Answer: Insipid : Taste
Explanation:
A nebulous from means having an ambiguous from same as an insipid taste which is dull, boring, almost no taste.
Correct Answer: 30
Explanation:
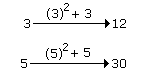
Correct Answer: Sand
Explanation:
As paper is product of tree. Similarly glass is product of sand.
Correct Answer:
Explanation:
if both I and II are implicit.
Correct Answer: Cruel
Explanation:
'Tall' is opposite to 'Dwarf' and 'Cruel' is opposite to kind.
Correct Answer: Traitor
Explanation:
Former cannot be expected from the latter.
Correct Answer:
Explanation:
H < T ...(i) T ? B ...(ii) B > R ...(iii)
From (i) and (ii) we get H < T ? B or B > H.
Hence III does not follow.
Correct Answer: NOPQ
Explanation:
Fill the blank space with correct alphabets as NOPQ word is repeating.
N O P Q , N O P Q, N O P Q, N O P Q ? NOPQ
Comments
There are no comments.More in Verbal Reasoning:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
