Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics and Communication Engineering ‣ Matching Questions See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Match the following:
List I List II A. Copper 1. produces discrete energy level just above valence band B. Rubber 2. produces discrete energy level just below conduction band C. Antimony 3. large forbidden gap D. Boron 4. valence and conduction bands overlap
Options- A. A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
- B. A-4, B-1, C-2, D-3
- C. A-4, B-3, C-1, D-2
- D. A-2, B-1, C-3, D-4
- Correct Answer
- A-4, B-3, C-1, D-2
- 1. Tesla is a unit of
Options- A. flux
- B. field strength
- C. flux density
- D. MMF Discuss
- 2. In a receiver, which of the following device has IF input but RF output?
Options- A. Demodulator
- B. Loudspeaker
- C. Audio amplifier
- D. Frequency changer Discuss
- 3. In Fermi-Dirac statistics, the probability of electron occupation of an energy level equal to Fermi level is
Options- A. 0
- B. 0.25
- C. 0.5
- D. 1 Discuss
- 4. In a shield helix
Options- A. the spacing between adjacent turns is very large
- B. the spacing between adjacent turns approaches zero
- C. the spacing between adjacent turns approaches zero and wire thickness approaches zero
- D. the spacing between adjacent turns is very large wire thickness approaches zero Discuss
- 5. Match the following:
List I List II A. 200 MHz 1. SHF B. 20 GHz 2. UHF C. 500 kHz 3. VHF D. 500 MHz 4. MF
Options- A. A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
- B. A-3, B-2, C-4, D-1
- C. A-3, B-4, C-1, D-2
- D. A-3, B-4, C-2, D-1 Discuss
- 6. A line of characteristic impedance Z0 branches into two line each with characteristic impedance Z0. The refracted voltage is
Options- A. zero
- B. infinite
- C. equal to incident voltage
- D. two third of incident voltage Discuss
- 7. Iron has a body centred cubic structure.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 8. A surge voltage
Options- A. has very high magnitude and very long duration
- B. has very high magnitude and very small duration
- C. has very high magnitude and very small duration and can be positive or negative
- D. can be only positive Discuss
- 9. The Ohm's law for conduction in metals is
Options- A. J = ?E
- B. J =
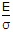
- C. J ? ?E
- D. J ?
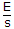 Discuss
Discuss
- 10. The following components are used to measure power output of a 2 kW TWT amplifier
- TWT
- Low pass/High pass filter
- Low power 20 dB attenuator
- 40 dB directional coupler with matched load
- Power meter.
Options- A. 1, 4, 2, 3, 5
- B. 1, 3, 4, 2, 5
- C. 1, 2, 4, 3, 5
- D. 1, 4, 3, 2, 5 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: flux density
Correct Answer: Demodulator
Correct Answer: 0.5
Correct Answer: the spacing between adjacent turns approaches zero and wire thickness approaches zero
Correct Answer: A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
Correct Answer: two third of incident voltage
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: has very high magnitude and very small duration and can be positive or negative
Correct Answer: J = ?E
Correct Answer: 1, 3, 4, 2, 5
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
