Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics and Communication Engineering ‣ Matching Questions See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Match the following:
List I List II A. Digital counter 1. Measurement of harmonics B. Schering Bridge 2. Measurement of frequency C. Meggar 3. Measurement of loss angle of dielectric D. Spectrum analyser 4. Measurement of insulation resistance
Options- A. A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
- B. A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
- C. A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
- D. A-4, B-1, C-3, D-2
- Correct Answer
- A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
- 1. Schrodinger wave equation is partial differential equation.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 2. The output frequency of a cycloconverter can be changed by changing the firing angle.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. Most of the memory chips in static RAM
Options- A. do not require any supply
- B. need 2 V supply
- C. need 5 V supply
- D. need 12 V supply Discuss
- 4. In crystalline solids, atoms are stacked in a regular manner.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 5. The classes of solid dielectrics are
Options- A. A, B, C, D, E, F, H
- B. A E B F H C D
- C. Y A E B F H C
- D. A E B F H C Discuss
- 6. The unit for mmf is
Options- A. A
- B. Wb
- C. T
- D. V Discuss
- 7. In a single phase full wave regulator, the firing angles in the positive and negative half cycles are generally
Options- A. equal
- B. different
- C. equal or different
- D. different but sometimes equal Discuss
- 8. The real part of complex dielectric constant and tan? for a dielectric are 2.1 and 5 x 10-4 at 100 Hz respectively. The imaginary part of dielectric constant at 100 Hz is
Options- A. 1.05 x 10-3
- B. 2.1 x 10-3
- C. 5 x 10-3
- D. 1.05 x 10-2 Discuss
- 9. The units for ?r are
Options- A. Farads
- B. Farads/m
- C.
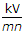
- D. no units Discuss
- 10. Tesla is a unit of
Options- A. flux
- B. field strength
- C. flux density
- D. MMF Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: need 5 V supply
Explanation:
Digital chips need 5 V supply.
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: Y A E B F H C
Correct Answer: A
Correct Answer: equal
Explanation:
Firing angles are kept equal to get symmetrical output voltage.
Correct Answer: 1.05 x 10-3
Explanation:
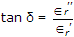
Correct Answer: no units
Explanation:
?r is only a numeric. Hence no units.
Correct Answer: flux density
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
