Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics and Communication Engineering ‣ Microwave Communication See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
In a klystron amplifier the bunching effect
Options- A. converts velocity modulation into current modulation of beam
- B. converts current modulation into velocity modulation of beam
- C. both (c) and (b)
- D. neither (a) nor (b)
- Correct Answer
- converts velocity modulation into current modulation of beam
ExplanationA Klystron is a vacuum tube used for generation/amplification of microwaves.An electron beam is produced by oxide coated indirectly heated cathode and is focussed and accelerated by focussing electrode.
This beam is transmitted through a glass tube. The input cavity where the beam enters the glass tube is called buncher.
As electrons move ahead they see an accelerating field for half cycle and retarding field for the other half cycle.
Therefore, some electrons are accelerated and some are retarded. This process is called velocity modulation.
The velocity modulation causes bunching of electrons. This bunching effect converts velocity modulation into density modulation of beam.
The input is fed at buncher cavity and output is taken at catcher cavity.
In a two cavity klystron only buncher and catcher cavity are used. In multi cavity klystron one or more intermediate cavities are also used.
The features of a multicavity klystron are :
1. Frequency range - 0.25 GHz to 100 GHz
2. Power output - 10 kW to several hundred kW
3. Power gain - 60 dB (nominal value)
4. Efficiency - about 40%.
A multicavity klystron is used in UHF TV transmitters, Radar transmitter and satellite communication.
More questions
- 1. Which device has internal positive feedback?
Options- A. Two cavity klystron amplifier
- B. Multi-cavity klystron amplifier
- C. Reflex klystron amplifier
- D. All of the above Discuss
Correct Answer: Reflex klystron amplifier
Explanation:
A Klystron is a vacuum tube used for generation/amplification of microwaves.An electron beam is produced by oxide coated indirectly heated cathode and is focussed and accelerated by focussing electrode.
This beam is transmitted through a glass tube. The input cavity where the beam enters the glass tube is called buncher.
As electrons move ahead they see an accelerating field for half cycle and retarding field for the other half cycle.
Therefore, some electrons are accelerated and some are retarded. This process is called velocity modulation.
The velocity modulation causes bunching of electrons. This bunching effect converts velocity modulation into density modulation of beam.
The input is fed at buncher cavity and output is taken at catcher cavity.
In a two cavity klystron only buncher and catcher cavity are used. In multi cavity klystron one or more intermediate cavities are also used.
The features of a multicavity klystron are :
1. Frequency range - 0.25 GHz to 100 GHz
2. Power output - 10 kW to several hundred kW
3. Power gain - 60 dB (nominal value)
4. Efficiency - about 40%.
A multicavity klystron is used in UHF TV transmitters, Radar transmitter and satellite communication.
- 2. Microwaves
Options- A. get reflected by ionosphere
- B. are absorbed by ionosphere
- C. are neither reflected nor absorbed by ionosphere
- D. are both reflected and absorbed by ionosphere Discuss
Correct Answer: are neither reflected nor absorbed by ionosphere
- 3. Consider the common emitter amplifier shown below with the following circuit parameters: ? = 100, gm = 0.3861 A/V, r0 = ? rp = 259 ?, Rs = 1 k?, RB = 93 k?, RC = 250 ?, RL = 1 kW, C1 = ? and C2 = 4.7mF.
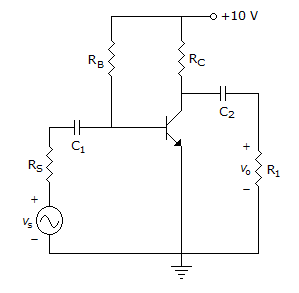
The resistance seen by the source Vs is
Options- A. 258 ?
- B. 1258 ?
- C. 93 k?
- D. ? Discuss
Correct Answer: 1258 ?
Explanation:
Zs = Rs + (RB || Brs)rc = 2.475 = 1.258 kV
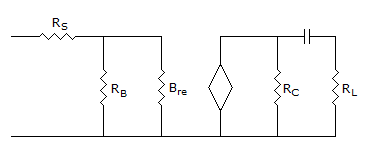
- 4. Push pull amplifier is
Options- A. voltage amplifier
- B. current amplifier
- C. power amplifier
- D. none of the above Discuss
Correct Answer: power amplifier
Explanation:
Push pull is a power amplifier.- 5. For a polyatomic gas, the equation relating dielectric constant ?r with molecular properties is
Options- A.
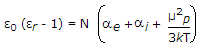
- B.
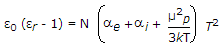
- C.
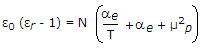
- D.
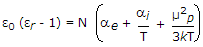 Discuss
Discuss
Correct Answer: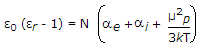
- 6. Assertion (A): For most metals, Fermi energy EF is less than 10 eV.
Reason (R): Fermi level of a metal is given by EF = 3.64 x 10-19 (n)2/3 where n is number of free electrons/m3 of metal.
Options- A. Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A
- B. Both A and R are true but R is not correct explanation of A
- C. A is true but R is false
- D. A is false but R is true Discuss
Correct Answer: Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A
- 7. Assertion (A): Copper is a good conductor of electricity.
Reason (R): Copper has a face centred cubic lattice.
Options- A. Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A
- B. Both A and R are true but R is not correct explanation of A
- C. A is true but R is false
- D. A is false but R is true Discuss
Correct Answer: Both A and R are true but R is not correct explanation of A
Explanation:
Conductivity does not depend on lattice structure.- 8. For a multiplate capacitor having n plates, A as area of each plate, the capacitance is proportional to
Options- A. n A
- B. (n - 1) A
- C. (n + 1) A
- D.
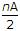 Discuss
Discuss
Correct Answer: (n - 1) A
Explanation:
If the number of plates is n, the number of capacitors is (n - 1).- 9. In rectifier circuits, the rms value of ac component of output voltage is equal to
Options- A. Vrms
- B. 0.5 Vrms
- C. (Vrms - Vdc)0.5
- D. (Vrms2 - Vdc2)0.5 Discuss
Correct Answer: (Vrms2 - Vdc2)0.5
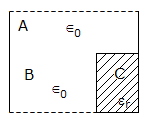
- 10. Figure shows a composite capacitor. If CA, CB, CC are the capacitances of capacitors A, B, C, the overall capacitance C is
Options- A. C = CA + CB + CC
- B. C = (CA + CB) CC
- C. C =
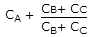
- D. C =
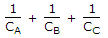 Discuss
Discuss
Correct Answer: C =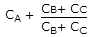
Explanation:
B and C are in series and A is in parallel with this combination.
Comments
There are no comments.
More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
