Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics and Communication Engineering ‣ Microwave Communication See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Power gain of a multicavity klystron amplifier is
Options- A. more than 30 dB
- B. causes retardation of all electrons
- C. causes acceleration of some electrons and retardation of others
- D. none of the above
- Correct Answer
- more than 30 dB
ExplanationA Klystron is a vacuum tube used for generation/amplification of microwaves.An electron beam is produced by oxide coated indirectly heated cathode and is focussed and accelerated by focussing electrode.
This beam is transmitted through a glass tube. The input cavity where the beam enters the glass tube is called buncher.
As electrons move ahead they see an accelerating field for half cycle and retarding field for the other half cycle.
Therefore, some electrons are accelerated and some are retarded. This process is called velocity modulation.
The velocity modulation causes bunching of electrons. This bunching effect converts velocity modulation into density modulation of beam.
The input is fed at buncher cavity and output is taken at catcher cavity.
In a two cavity klystron only buncher and catcher cavity are used. In multi cavity klystron one or more intermediate cavities are also used.
The features of a multicavity klystron are :
1. Frequency range - 0.25 GHz to 100 GHz
2. Power output - 10 kW to several hundred kW
3. Power gain - 60 dB (nominal value)
4. Efficiency - about 40%.
A multicavity klystron is used in UHF TV transmitters, Radar transmitter and satellite communication.
More questions
- 1. An RC snubber circuit is used to protect a thyristor against :
Options- A. false triggering
- B. failure to turn on
- C. switching transients
- D. failure to commutate Discuss
Correct Answer: switching transients
Explanation:
Especially high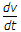 during switching.
during switching.
- 2. The displacement flux density at a point on the surface of a perfect conductor is
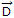 = 2(ax - 3 az)c/m2 pointing away from the surface. The charge density at that point c/m2 will be
= 2(ax - 3 az)c/m2 pointing away from the surface. The charge density at that point c/m2 will be
Options- A. 2
- B. - 2
- C. 4
- D. - 4 Discuss
Correct Answer: 4
Explanation:
? . D = r.- 3. To increase Q factor of a coil, the wire should be
Options- A. long
- B. thin
- C. thick
- D. long and thin Discuss
Correct Answer: thick
Explanation:
Q is high if resistance is low. Therefore, wire should be thick.- 4. Match the following:
List I (DOS commands) List II (Meaning) A. ATTRIB 1. Displays all directories and subdirectories B. SCAN DISK 2. Moves files to another director C. MOVE 3. Checks the status of disc D. TREE 4. Hides a file
Options- A. A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
- B. A-3, B-4, C-2, D-1
- C. A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
- D. A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1 Discuss
Correct Answer: A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
- 5. Match the following:
List I List II A. SSB Modulation 1. Transmission line B. ? . B = 0 2. Hilbert transform C. Model dispersion 3. Faraday's law 4. Absence of magnetic monopoles 5. Waveguides 6. Phase locked loop
Options- A. A-1, B-3, C-5
- B. A-5, B-4, C-2
- C. A-6, B-4, C-5
- D. A-2, B-4, C-5 Discuss
Correct Answer: A-2, B-4, C-5
- 6. Match the following:
List I List II A. 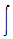 (? x E)ds = 0
(? x E)ds = 01. Continuity equation B. 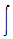 rv.dv = Q
rv.dv = Q2. Ampere's law C. 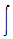 (J + D)ds
(J + D)ds3. Gauss law D. - 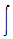 rvdv
rvdv4. Faraday's law E. 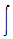 H.dl =
H.dl = 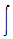 (? x H)ds
(? x H)ds5. Stoke's theorem
Options- A. A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1, E-5
- B. A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4, E-5
- C. A-4, B-2, C-1, D-3, E-5
- D. A-1, B-5, C-4, D-2, E-3 Discuss
Correct Answer: A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1, E-5
- 7. Match the following:
List I (Command in WORD) List II (Meaning) A. END 1. The bar displays the current position of cursor B. HOME 2. Moves cursor to the beginning of current line C. Status 3. Moves cursor to end of document
Options- A. A-1, B-2, C-3
- B. A-3, B-1, C-2
- C. A-2, B-3, C-1
- D. A-3, B-2, C-1 Discuss
Correct Answer: A-3, B-2, C-1
- 8. Match the following:
List I List II A. Penetration frequency 1. Lowest frequency at which charged particles spiral in fixed magnetic field B. Optimum working frequency 2. Same as critical and frequency C. Gyro frequency 3. Highest frequency of radio waves that can be used D. Maximum usable frequency 4. The most effective frequency for ionosphere propagation of radio waves
Options- A. A-2, B-4, C-1, D-3
- B. A-4, B-1, C-3, D-2
- C. A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4 Discuss
Correct Answer: A-2, B-4, C-1, D-3
- 9. Match the following:
List I List II A. Output of signal generator 1. Modulated B. Error signal from a synchro 2. Digital C. Output of a JK flip flop 3. Analog D. Signal received by radar 4. Stoichastic
Options- A. A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
- B. A-3, B-1, C-2, D-4
- C. A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
- D. A-1, B-3, C-4, D-2 Discuss
Correct Answer: A-3, B-1, C-2, D-4
- 10. Match the following:
List I List II A. TV 1. 1 kHz B. Radio 2. 3 kHz C. Telephony 3. 9 kHz D. Telegraphy 4. 5 MHz
Options- A. A-4, B-1, C-2
- B. A-4, B-3, C-2
- C. A-2, B-1, C-3
- D. A-1, B-2, C-3 Discuss
Correct Answer: A-4, B-3, C-2
Comments
There are no comments.
More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
