Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics and Communication Engineering ‣ Power Electronics See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
In a single phase dual converter, a1, and a2 are firing angles of the two converters. Then
Options- A. a1 - a2 =
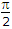
- B. a1 + a2 = p
- C. a1 - a2 = p
- D. a1 + a2 =
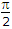
- Correct Answer
- a1 + a2 = p
ExplanationSince one converter is rectifying and the other is invertingVdc1 = -Vdc2
or a1 + a2 = p.
More questions
- 1. The number of protons in germanium atom is
Options- A. 4
- B. 16
- C. 28
- D. 32 Discuss
Correct Answer: 32
- 2. A low ratio of the A.C. load impedance of a diode detector results in
Options- A. diagonal clipping
- B. poor AGC operation
- C. poor AF response
- D. negative peak clipping Discuss
Correct Answer: negative peak clipping
- 3. To produce magnetic flux, mmf is necessary.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: True
- 4. The units of ?0 and ?r are
Options- A. H/m for both
- B. H/m for ?r and no units for ?0
- C. H/m for ?0 and no units for ?r
- D. Wb/m for ?0 and no units for ?r Discuss
Correct Answer: H/m for ?0 and no units for ?r
Explanation:
?r is only a numeric.- 5. An unmodulated voltage 10 V effective is applied to a dioxide detector in which load resistance is 4 x 10-5 ohms. A micrometer shows that the rectified DC current in this resistance is 30 A. The efficiency of detection is
Options- A. 34%
- B. 55.5%
- C. 68.8%
- D. 84.7% Discuss
Correct Answer: 84.7%
- 6. Some typical examples of macroscopic quantities are
Options- A. conductivity
- B. µr
- C. dielectric constant
- D. all of the above Discuss
Correct Answer: all of the above
- 7. Nichrome is used for
Options- A. overload line wires
- B. heater coils
- C. lamp filaments
- D. all of the above Discuss
Correct Answer: heater coils
Explanation:
Because heater coil must be made of high resistivity material.- 8. Yettrium-iron garnet (Y2Fe5O12) is a soft magnetic material suitable for applications involving
Options- A. dc
- B. 50 Hz ac
- C. ac of a few K Hz
- D. ac of a few hundred MHz Discuss
Correct Answer: dc
Explanation:
Yettrium iron garnet has very low eddy current loss. Hence it is used at frequencies in MHz range.- 9. Which of the following is used in automatic control of street lights?
Options- A. Thermistor
- B. Photoconductor
- C. Transistor
- D. Varistor Discuss
Correct Answer: Photoconductor
- 10. A leaky dielectric has ?r = ?r' - j?r". If a field E is applied, the current component in phase with E is proportional to ?r".
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: True
Comments
There are no comments.
More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
