Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics and Communication Engineering ‣ Satellite Communication See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
A typical signal strength received from a geosynchronous communication satellite is of the order of a few
Options- A. milliwatts
- B. kilowatts
- C. picowatts
- D. watts
- Correct Answer
- picowatts
- 1. Match the following:
List I List II A. SSB Modulation 1. Transmission line B. ? . B = 0 2. Hilbert transform C. Model dispersion 3. Faraday's law 4. Absence of magnetic monopoles 5. Waveguides 6. Phase locked loop
Options- A. A-1, B-3, C-5
- B. A-5, B-4, C-2
- C. A-6, B-4, C-5
- D. A-2, B-4, C-5 Discuss
- 2. Match the following:
List I List II A. 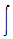 (? x E)ds = 0
(? x E)ds = 01. Continuity equation B. 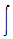 rv.dv = Q
rv.dv = Q2. Ampere's law C. 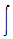 (J + D)ds
(J + D)ds3. Gauss law D. - 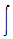 rvdv
rvdv4. Faraday's law E. 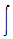 H.dl =
H.dl = 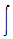 (? x H)ds
(? x H)ds5. Stoke's theorem
Options- A. A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1, E-5
- B. A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4, E-5
- C. A-4, B-2, C-1, D-3, E-5
- D. A-1, B-5, C-4, D-2, E-3 Discuss
- 3. Match the following:
List I (Command in WORD) List II (Meaning) A. END 1. The bar displays the current position of cursor B. HOME 2. Moves cursor to the beginning of current line C. Status 3. Moves cursor to end of document
Options- A. A-1, B-2, C-3
- B. A-3, B-1, C-2
- C. A-2, B-3, C-1
- D. A-3, B-2, C-1 Discuss
- 4. Match the following:
List I List II A. Penetration frequency 1. Lowest frequency at which charged particles spiral in fixed magnetic field B. Optimum working frequency 2. Same as critical and frequency C. Gyro frequency 3. Highest frequency of radio waves that can be used D. Maximum usable frequency 4. The most effective frequency for ionosphere propagation of radio waves
Options- A. A-2, B-4, C-1, D-3
- B. A-4, B-1, C-3, D-2
- C. A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4 Discuss
- 5. Match the following:
List I List II A. Output of signal generator 1. Modulated B. Error signal from a synchro 2. Digital C. Output of a JK flip flop 3. Analog D. Signal received by radar 4. Stoichastic
Options- A. A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
- B. A-3, B-1, C-2, D-4
- C. A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
- D. A-1, B-3, C-4, D-2 Discuss
- 6. Match the following:
List I List II A. TV 1. 1 kHz B. Radio 2. 3 kHz C. Telephony 3. 9 kHz D. Telegraphy 4. 5 MHz
Options- A. A-4, B-1, C-2
- B. A-4, B-3, C-2
- C. A-2, B-1, C-3
- D. A-1, B-2, C-3 Discuss
- 7. The normal operation of JFET is
Options- A. constant voltage region
- B. constant current region
- C. both constant voltage and constant current regions
- D. either constant voltage or constant current region Discuss
- 8. Assertion (A): McMurray Bredford half bridge inverter uses complementary commutation
Reason (R): Three phase inverter can have two modes of operation.
Options- A. Both A and R are correct and R is correct explanation of A
- B. Both A and R correct but R is not correct explanation of A
- C. A is correct but R is wrong
- D. A is wrong but R is correct Discuss
- 9. Assuming a minimum angle of elevation of 5°, a geosynchronous satellite remains in line-of-sight for __________ percentage of Earth's surface.
Options- A. 30.3
- B. 42.4
- C. 50
- D. 25 Discuss
- 10. In a turnstile antenna two-half wave resonant wire radiators are placed at 90° to each other in the same plane and are excited
Options- A. in phase
- B. in phase opposition
- C. 90° out of phase with each other
- D. 45° out of phase with each other Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: A-2, B-4, C-5
Correct Answer: A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1, E-5
Correct Answer: A-3, B-2, C-1
Correct Answer: A-2, B-4, C-1, D-3
Correct Answer: A-3, B-1, C-2, D-4
Correct Answer: A-4, B-3, C-2
Correct Answer: constant current region
Explanation:
In major portion of drain characteristics ID is constant.
Correct Answer: Both A and R correct but R is not correct explanation of A
Correct Answer: 25
Correct Answer: 90° out of phase with each other
Explanation:
Since the two wire radiators are at 90° to each other, they have to be excited 90° out of phase with each other.
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
