Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics and Communication Engineering ‣ Materials and Components See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
A dielectric is subjected to alternating field. The dielectric losses are potential to
Options- A. real part of dielectric constant
- B. imaginary part of dielectric constant
- C. both real and imaginary parts of dielectric constant
- D. either real or imaginary part of dielectric constant
- Correct Answer
- imaginary part of dielectric constant
ExplanationAbsorption of energy is proportional to imaginary part of complex dielectric constant.
More questions
- 1. Schrodinger wave equation is partial differential equation.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: True
- 2. The output frequency of a cycloconverter can be changed by changing the firing angle.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: False
- 3. Most of the memory chips in static RAM
Options- A. do not require any supply
- B. need 2 V supply
- C. need 5 V supply
- D. need 12 V supply Discuss
Correct Answer: need 5 V supply
Explanation:
Digital chips need 5 V supply.- 4. In crystalline solids, atoms are stacked in a regular manner.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: True
- 5. The classes of solid dielectrics are
Options- A. A, B, C, D, E, F, H
- B. A E B F H C D
- C. Y A E B F H C
- D. A E B F H C Discuss
Correct Answer: Y A E B F H C
- 6. The unit for mmf is
Options- A. A
- B. Wb
- C. T
- D. V Discuss
Correct Answer: A
- 7. In a single phase full wave regulator, the firing angles in the positive and negative half cycles are generally
Options- A. equal
- B. different
- C. equal or different
- D. different but sometimes equal Discuss
Correct Answer: equal
Explanation:
Firing angles are kept equal to get symmetrical output voltage.- 8. The real part of complex dielectric constant and tan? for a dielectric are 2.1 and 5 x 10-4 at 100 Hz respectively. The imaginary part of dielectric constant at 100 Hz is
Options- A. 1.05 x 10-3
- B. 2.1 x 10-3
- C. 5 x 10-3
- D. 1.05 x 10-2 Discuss
Correct Answer: 1.05 x 10-3
Explanation:
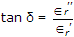
- 9. The units for ?r are
Options- A. Farads
- B. Farads/m
- C.
- D. no units Discuss
Correct Answer: no units
Explanation:
?r is only a numeric. Hence no units.- 10. Tesla is a unit of
Options- A. flux
- B. field strength
- C. flux density
- D. MMF Discuss
Correct Answer: flux density
Comments
There are no comments.
More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
