Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics and Communication Engineering ‣ Materials and Components See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
A material which is lightly repelled by a magnetic field is known as
Options- A. diamagnetic material
- B. non-magnetic material
- C. ferromagnetic material
- D. paramagnetic material
- Correct Answer
- diamagnetic material
- 1. In which region of a CE bipolar transistor is collector current almost constant?
Options- A. Saturation region
- B. Active region
- C. Breakdown region
- D. Both saturation and active region Discuss
- 2. The Q factor of a waveguide resonator is given by (?0 is resonant frequency, U is energy storage and WL is the power loss)
Options- A.
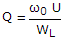
- B.
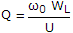
- C. Q = ?0UWL
- D.
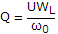 Discuss
Discuss
- 3. In a resistance strain gauge, G = 2, stress = 1050 kg/cm2, R = 1000 ?. The value of ?R will be
Options- A. 2 ?
- B. 3 ?
- C. 4 ?
- D. 1 ? Discuss
- 4. In a broadcast superheterodyne receiver
Options- A. the local oscillator operates below the signal frequency
- B. local oscillator frequency is normally double the IF
- C. RF amplifier normally works at kHz above the carrier frequency
- D. mixer input must be tuned to the signal frequency Discuss
- 5. FM receivers using the standard 88 to 108 MHz band use IF of
Options- A. 8 MHz
- B. 9.9 MHz
- C. 10.7 MHz
- D. 12.2 MHz Discuss
- 6. Which one of the following potential does not satisfy Laplace's equations?
Options- A. v = 10 xy
- B. v = p cos ?
- C.

- D. v = f cos ? + 10 Discuss
- 7. The rate at which information can be carried through a communication channel depends on
Options- A. carrier frequency
- B. bandwidth
- C. transmission loss
- D. transmitted power Discuss
- 8. Generally the wall thickness of rectangular waveguide is
Options- A. about 1-5 mils
- B. about 40-100 mils
- C. about 0.1 to 0.5 mils
- D. about 500 mils Discuss
- 9. It is known that noise phase modulates the FM wave. As the noise side band frequency approaches the carrier frequency, the noise amplitude
Options- A. will increase
- B. will decrease
- C. will remain constant
- D. will reduce to negligible value Discuss
- 10. Curie Weiss law is
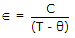 .
.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: Active region
Explanation:
It is used as amplifier when it operates in this region.
Correct Answer:
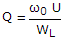
Correct Answer: 1 ?
Explanation:

 .
.
Correct Answer: mixer input must be tuned to the signal frequency
Correct Answer: 10.7 MHz
Correct Answer: v = p cos ?
Explanation:
 .
.
Correct Answer: bandwidth
Explanation:
Rate of information depends on bandwidth.
Correct Answer: about 40-100 mils
Correct Answer: will decrease
Correct Answer: True
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
