Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Highway Engineering See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The maximum distance of the apex of a vertical curve of length L from the point of intersection of two grades + g1%, and - g2% (g1 > g2), is
Options- A.
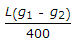
- B.
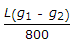
- C.
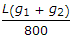
- D.
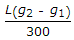
- Correct Answer
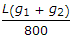
- 1. To have greatest coverage of the area, the type of photography used, is
Options- A. high oblique
- B. low oblique
- C. vertical
- D. none of these. Discuss
- 2. Excessive fluoride in drinking water causes
Options- A. Alzheimer's disease
- B. Mottling of teeth and embrittlement of bones
- C. Methemoglobinemia
- D. Skin cancer Discuss
- 3. Snowcrete is one of the patent forms of
Options- A. distempers
- B. water proof cement paints
- C. enamel paints
- D. cellulose paints. Discuss
- 4. To achieve best performance, the type of switch preferred to, is
Options- A. undercut switch
- B. straight-cut switch
- C. overriding switch
- D. both (a) and (b)
- E. none of these. Discuss
- 5. The standard dimensions of a wooden sleeper for a B.G. railway track are
Options- A. 2.74 m x 25 cm x 13 cm
- B. 1.83 m x 20 cm x 11 cm
- C. 1.52 m x 15 cm x 10 cm
- D. 1.75 cm x 20 cm x 12 cm
- E. none of these. Discuss
- 6. For preparing porcelains, the clay should be
Options- A. sufficiently pure
- B. of high degree of tanacity
- C. of good plasticity
- D. All the above. Discuss
- 7. If D is the distance between the parallel sidings and ? is the angle of crossing, the distance between the noses of crossing measured parallel to the main track, is
Options- A. D tan ?
- B. D sec ?
- C. D cosec ?
- D. D cot ? Discuss
- 8. If the difference in elevation of an edge of the pavement 9 m wide and its crown is 15 cm, the camber of the pavement, is
Options- A. 1 in 60
- B. 1 in 45
- C. 1 in 30
- D. 1 in 15
- E. 1 in 7.5 Discuss
- 9. The loose pockets in soil mass can be bridged safely by providing a raft foundation provided the soft area is smaller than
Options- A. the column spacing
- B. one-third the column spacing
- C. half the column spacing
- D. three-fourth the column spacing
- E. none of these. Discuss
- 10. The moment diagram for a cantilever whose free end is subjected to a bending moment, will be a
Options- A. triangle
- B. rectangle
- C. parabola
- D. cubic parabola. Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: high oblique
Correct Answer: Mottling of teeth and embrittlement of bones
Correct Answer: water proof cement paints
Correct Answer: overriding switch
Correct Answer: 2.74 m x 25 cm x 13 cm
Correct Answer: All the above.
Correct Answer: D cosec ?
Correct Answer: 1 in 30
Correct Answer: one-third the column spacing
Correct Answer: rectangle
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Advanced SurveyingAirport EngineeringApplied MechanicsBuilding ConstructionBuilding MaterialsConcrete TechnologyConstruction ManagementDocks and HarboursElements of Remote SensingEngineering EconomyEstimating and CostingGATE Exam QuestionsHighway EngineeringHydraulicsIrrigationRailwaysRCC Structures DesignSI UnitsSoil Mechanics and Foundation EngineeringSteel Structure DesignStrength of MaterialsStructural Design SpecificationsSurveyingTheory of StructuresTunnellingUPSC Civil Service Exam QuestionsWaste Water EngineeringWater Resources EngineeringWater Supply EngineeringProgramming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
