Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Highway Engineering See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
If N is the algebraic difference of grades, S is the head light beam distance in metres, the length (L) of a valley curve, is
Options- A.
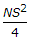
- B.
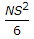
- C.
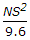
- D.
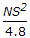
- E.
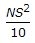
- Correct Answer
- 1. In scanty rainfall regions, the camber provided will be
Options- A. nil
- B. flatter
- C. steeper
- D. None of these. Discuss
- 2. The radius of curvature of the arc of the bubble tube is generally kept
Options- A. 10 m
- B. 25 m
- C. 50 m
- D. 100 m Discuss
- 3. The solid angles are measured in
Options- A. degrees
- B. grades
- C. radians
- D. steradians. Discuss
- 4. The absolute minimum sight distance required for stopping a vehicle moving with a speed of 80 km ph, is
Options- A. 120 m
- B. 200 m
- C. 640 m
- D. none of these. Discuss
- 5. The expected out turn of 12 mm plastering with cement mortar is
Options- A. 2.5 sq m
- B. 4.0 sq m
- C. 6.0 sq m
- D. 8.0 sq m
- E. 10 sq m Discuss
- 6. An ideal flow of a liquid obeys
Options- A. Continuity equation
- B. Newton's law of viscosity
- C. Newton's second law of motion
- D. dynamic viscosity law, Discuss
- 7. Attracting groynes are built
Options- A. perpendicular to the bank
- B. inclined down stream
- C. inclined up stream
- D. none of these. Discuss
- 8. All reinforcement should be free from
Options- A. loose mill scales
- B. loose rust
- C. paints
- D. oil
- E. all the above. Discuss
- 9. The pressure less than atmospheric , pressure, is known
Options- A. suction pressure
- B. vacuum pressure
- C. negative gauge pressure
- D. all the above. Discuss
- 10. The rainfall at any place is described by
Options- A. its intensity
- B. its duration
- C. its frequency
- D. all the above. Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: flatter
Correct Answer: 100 m
Correct Answer: steradians.
Correct Answer: 120 m
Correct Answer: 8.0 sq m
Correct Answer: Continuity equation
Correct Answer: inclined down stream
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: all the above.
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
