Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Highway Engineering See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
If N is the algebraic difference of grades, S is the minimum sight distance in metres, the length (L) of a summit curve is
Options- A.
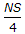
- B.
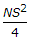
- C.
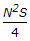
- D.
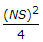
- E. none of these.
- Correct Answer
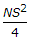
- 1. Water paint is a
Options- A. white wash
- B. colour wash
- C. whiting
- D. distemper
- E. all the above. Discuss
- 2. Minimum depth of ballast prescribed of B.G. trunk lines of Indian Railways, is
Options- A. 20 cm
- B. 15 cm
- C. 25 cm
- D. 30 cm
- E. 35 cm Discuss
- 3. You are given a sample of soil containing coarse grains to determine its water content, you will use
Options- A. pycnometer
- B. oven-drying method
- C. calcium carbide method
- D. alcohol method. Discuss
- 4. Pick up the incorrect statement from the following :
Options- A. In radial flow, fluid flows such that pressure and velocity at any point change with respect to its distance from the central axis
- B. In radial flow, velocity of flow is in a radial direction
- C. In radial flow, flow may take place radially inward to or outward from the centre
- D. In radial flow, flow is one dimensional with stream lines parallel. Discuss
- 5. A fall which maintains its depth, is
Options- A. a trapezoidal notch fall
- B. a low weir fall
- C. a rectangular notch fall
- D. all the above. Discuss
- 6. Slump test is done for
Options- A. clay
- B. sand
- C. lime
- D. concrete. Discuss
- 7. Rankine-Golden formula accounts for direct as well as buckling stress and is applicable to
Options- A. very long columns
- B. long columns
- C. short columns
- D. intermediate columns
- E. all the above. Discuss
- 8. Design of highways is based on
Options- A. axle loads
- B. axle spacings
- C. wheel bases
- D. over all length
- E. all the above. Discuss
- 9. The ratio of the length of long chord and the tangent length of a circular curve of radius R deflecting through angle ?, is
Options- A. sin
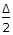
- B. cos
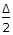
- C. tan
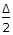
- D. 2 sin
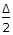
- E. 2 cos
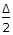 .
Discuss
.
Discuss
- 10. The ratio of maximum sewage flow to average sewage flow for mains up to 1 m in diameter, is
Options- A. 1.5
- B. 2.0
- C. 3.0
- D. 4.0 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: 25 cm
Correct Answer: pycnometer
Correct Answer: In radial flow, flow is one dimensional with stream lines parallel.
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: concrete.
Correct Answer: intermediate columns
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: 2 cos
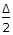 .
. Correct Answer: 2.0
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
