Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Water Resources Engineering Comments
- Question
Pick up the correct statement from the following :
Options- A. If ground water enters the channel, the channel is known as effulent channel
- B. If water goes out of channel to meet ground water, the channel is said to be influent stream
- C. If the water table is at higher level than the water level in channel, ground water flows to the stream
- D. If the water level in stream is higher than the water table level, water from the channel enters into ground water
- E. All the above.
- Correct Answer
- All the above.
- 1. The rate of evaporation from reservoirs may be determined by
Options- A. pan-measurement method
- B. empirical formulae
- C. storage equation method
- D. energy budget method
- E. all the above. Discuss
- 2. Relative humidity is the ratio of actual vapour pressure to the saturation vapour pressure
Options- A. at the same temperature
- B. at the same pressure
- C. in the same volume
- D. in the atmosphere. Discuss
- 3. For efficient working of a control meter, its throat length is approximately kept
Options- A. equal to the critical depth
- B. twice the critical depth
- C. three times the critical depth
- D. four times the critical depth. Discuss
- 4. Ryve's formula for flood estimate in cumecs, is
Options- A. Q = CA3/4
- B. Q = CA2/3
- C. Q = CA1/2
- D. Q = CA1/4. Discuss
- 5. The area enclosed by the adjacent isohyets of a catchment basin are shown under :
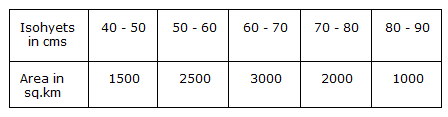
The average depth of annual precipitation in the catchment basin will be
Options- A. 60.0 cm
- B. 60.5 cm
- C. 61.5 cm
- D. 62.5 cm
- E. 63.5 cm. Discuss
- 6. If ? is unit weight of water, Q the discharge in cumecs, H the total head lift and ?, the efficiency of the pump, the H.P. of the motor is
Options- A.
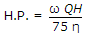
- B.
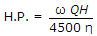
- C.
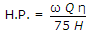
- D.
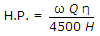 Discuss
Discuss
- 7. A soil strata may consist of
Options- A. soil zone
- B. intermediate zone
- C. capillary zone
- D. ground water zone
- E. all the above. Discuss
- 8. Isopiastic lines are the contours
Options- A. drawn to represent water table
- B. drawn to represent piezometric heads
- C. drawn to piezometric surface
- D. none of these. Discuss
- 9. Run off is measured in
Options- A. cubic metres
- B. cubic metres per sec.
- C. cubic metres per minute
- D. cubic metres per hour. Discuss
- 10. Dicken's formula for high flood estimate, is useful only for the catchments in
Options- A. Southern India
- B. Northern India
- C. Eastern India
- D. Western India. Discuss
Water Resources Engineering problems
Search Results
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: at the same temperature
Correct Answer: three times the critical depth
Correct Answer: Q = CA2/3
Correct Answer: 63.5 cm.
Correct Answer:
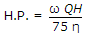
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: drawn to piezometric surface
Correct Answer: cubic metres per sec.
Correct Answer: Northern India
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
