Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Strength of Materials See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The width b and depth d of a beam cut from a wooden cylindrical log of 100 cm diameter for maximum strength are :
Options- A. b = 57.73 cm d = 81.65 cm
- B. b = 81.65 cm d = 57.73 cm
- C. b = 50.00 cm d = 50.00 cm
- D. b = 40.00 cm d = 80.00 cm
- E. b = 30.00 cm d = 60.00 cm.
- Correct Answer
- b = 57.73 cm d = 81.65 cm
- 1. Lami's theroem states that
Options- A. three forces acting at a point are always in equilibrium
- B. if three forces acting on a point can be represented in magnitude and direction by the sides of a triangle, the point will be in the state of equilibrium
- C. three coplaner forces acting at a point will be in equilibrium, if each force is proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two
- D. three coplaner forces acting at a point will be in equilibrium if each force is inversely proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two
- E. none of these. Discuss
- 2. If d and n are the effective depth and depth of the neutral axis respectively of a singly reinforced beam, the lever arm of the beam, is
Options- A. d
- B. n
- C.
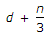
- D.
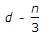
- E.
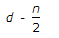 Discuss
Discuss
- 3. The rate of accumulation of sludge per person per year, is
Options- A. 10 litres
- B. 15 litres
- C. 20 litres
- D. 25 litres
- E. 30 litres. Discuss
- 4. For a single section used as a tension member, the given area is assumed
Options- A. 20% to 30% in excess of the net area
- B. 30% to 40% in excess of the net area
- C. 40% to 50% in excess of the net area
- D. 50% to 60% in excess of the net area
- E. 60% to 70% in excess of the net area. Discuss
- 5. Pick up the correct statement from the following:
Options- A. Pointing is measured in sq.m
- B. Plastering is measured in sq.m
- C. Glazing is measured in sq.m
- D. Striking is measured in sq.m
- E. All the above. Discuss
- 6. A current meter measures the velocity of flow, if it is held
Options- A. on the surface of water
- B. at the bottom of channel
- C. at any point within the cross-section
- D. none of these. Discuss
- 7. If the coefficients of volume change and compressibility of a soil sample are respectively 6.75 x 10-2 and 3 x 10-2, the void ratio of the soil sample, is
Options- A. 1.10
- B. 1.15
- C. 1.20
- D. 1.25
- E. 1.30 Discuss
- 8. The presence of free ammonia in sewage, is detected by
Options- A. boiling
- B. adding pottassium permanganate
- C. adding sulphuric acid
- D. phenol-di-sulphuric acid. Discuss
- 9. The maximum area of compression reinforcement in a beam of cross section B x D is limited to
Options- A. 0.02 BD
- B. 0.03 BD
- C. 0.04 BD
- D. 0.05 BD Discuss
- 10. Dado is usually provided in
Options- A. dinning halls
- B. bath rooms
- C. living rooms
- D. verandah
- E. roofs. Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: three coplaner forces acting at a point will be in equilibrium, if each force is proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two
Correct Answer:
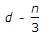
Correct Answer: 20 litres
Correct Answer: 40% to 50% in excess of the net area
Correct Answer: All the above.
Correct Answer: at any point within the cross-section
Correct Answer: 1.25
Explanation:
Coeff.compressibility = Coeff.volume change/(1 + e).
(1 + e) = Coeff.volume change/Coeff.compressibility.
e = (Coeff.volume change/Coeff.compressibility) - 1.
e = ((6.75 x 10-2)/(3 x 10-2)) - 1.
e = 2.25 - 1.
e = 1.25.
Correct Answer: boiling
Correct Answer: 0.04 BD
Correct Answer: bath rooms
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
