Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Concrete Technology See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The surface where two successive placements of concrete meet, is known as
Options- A. Contraction joint
- B. Expansion joint
- C. Construction joint
- D. both (a) and (b)
- E. both (6) and (c).
- Correct Answer
- Construction joint
- 1. The greatest eccentricity which a load W can have without producing tension on the cross-section of a short column of external diameter D and internal diameter d, is
Options- A.
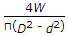
- B.
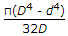
- C.
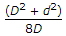
- D.
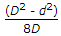
- E.
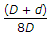 Discuss
Discuss
- 2. Pick up the correct statement from the following :
Options- A. The distance between two successive crests or troughs of a wave, is called, the wave length
- B. The wave length is measured in metres and a fraction of a metre
- C. The wave length is generally denoted by ?
- D. The length of the crest from the mid point, is called amplitude
- E. All of these Discuss
- 3. Pick up the correct statement from the following:
Options- A. Uniform series compound amount factor =
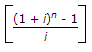
- B. Uniform series present worth factor =
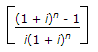
- C. Sinking fund factor =
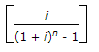
- D. Capital recovery factor =
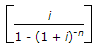 where letters carry their usual meanings.
where letters carry their usual meanings. - E. All of these Discuss
- 4. The correction applied to the measured base of length L is
Options- A.
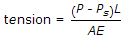
- B.
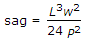 where w is the weight of tape/m
where w is the weight of tape/m - C.
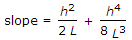 where h is height difference of end supports
where h is height difference of end supports - D. Reduction to mean sea level =
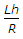
- E. all the above. Discuss
- 5. For an ordinary Portland cement
Options- A. residual does not exceed 10% when sieved through IS Sieve No. 9
- B. soundness varies from 5 to 10 mm
- C. initial setting time is not less than 30 minutes
- D. compressive stress after 7 days, is not less than 175 kg/cm2
- E. all the above. Discuss
- 6. Pick up the correct statement from the following:
Options- A. Permeability is a measure of conducting the magnetic lines of force in the material.
- B. Permeability is a measure of the extent to which magnetic lines of force can penetrate a medium.
- C. Permeability is expressed as the ratio of the magnetic flux density (B) to the field strength of the magnetizing field.
- D. The force between the magnetic poles is inversely proportional to the permeability of the medium.
- E. All of these Discuss
- 7. M - ? relationship for a simply supported beam shown below is given by :
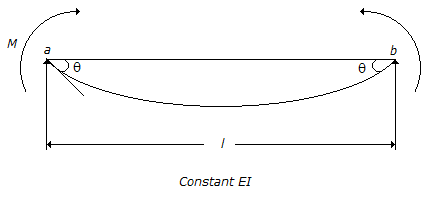
Options- A. M l/EI = 2?
- B. M l/EI = 3?
- C. M l/EI = 4?
- D. M l/EI = 6? Discuss
- 8. The altitude of a heavenly body is its angular distance, measured on the vertical circle passing through the body, above
Options- A. equator
- B. horizon
- C. pole
- D. none of these. Discuss
- 9. The difference in longitude of two places expressed in time is equal to the difference in their
Options- A. sidereal time
- B. apparent solar time
- C. mean solar time
- D. all the above. Discuss
- 10. Design rate of super elevation for horizontal highway curve of radius 450 m for a mixed traffic condition, having a speed of 125 km/hour is
Options- A. 1.0
- B. 0.05
- C. 0.07
- D. 0.154 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer:
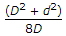
Correct Answer: All of these
Correct Answer: All of these
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: initial setting time is not less than 30 minutes
Correct Answer: All of these
Correct Answer: M l/EI = 4?
Correct Answer: horizon
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: 0.154
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
