Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Concrete Technology See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Pick up the correct statement from the following:
Options- A. An increase in water content must be accompanied by an increase in cement content
- B. Angular and rough aggregates reduce the workability of the concrete
- C. Large size aggregates increase the workability due to lesser surface area
- D. The slump of the concrete mix decreases due to an increase in temperature
- E. All the above.
- Correct Answer
- All the above.
- 1. An ordinary Portland cement when tested for its fineness, should not leave any residue on I.S. seive No. 9, more than
Options- A. 5%
- B. 10%
- C. 15%
- D. 20%
- E. 25% Discuss
- 2. The ratio of circumferential stress to the longitudinal stress in the walls of a cylindrical shell, due to flowing liquid, is
Options- A.
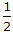
- B. 1
- C.
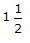
- D. 2 Discuss
- 3. Biochemical Oxygen Demand (B.O.D.) of safe drinking water must be
Options- A. nil
- B. 5
- C. 10
- D. 15
- E. 20 Discuss
- 4. The minimum percentage of chemical ingredient of cement is that of
Options- A. magnesium oxide
- B. iron oxide
- C. alumina
- D. lime
- E. silica. Discuss
- 5. The rainfall cycle period in India is taken as
Options- A. 15 years
- B. 20 years
- C. 25 years
- D. 30 years
- E. 35 years. Discuss
- 6. Concrete containing
Options- A. silicious aggregates, has higher co-efficient of expansion
- B. igneous aggregates, has intermediate coefficient of expansion
- C. lime stones, has lowest co-efficient of expansion
- D. All the above. Discuss
- 7. Most commonly used solvent in oil paints, is
Options- A. petroleum
- B. spirit
- C. coaltar
- D. turpentine. Discuss
- 8. Stones used for rubble masonry must be
Options- A. soft
- B. hard
- C. light
- D. heavy. Discuss
- 9. In railways a triangle is mainly provided for
Options- A. diverting trains from the main line to branch line
- B. crossing over between parallel tracks
- C. changing direction of engines through 180°
- D. shunting wagons in yards. Discuss
- 10. The most economical section for a column, is
Options- A. rectangular
- B. solid round
- C. flat strip
- D. tubular section
- E. hexagonal. Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 10%
Correct Answer: 2
Correct Answer: nil
Correct Answer: magnesium oxide
Correct Answer: 35 years.
Correct Answer: All the above.
Correct Answer: petroleum
Correct Answer: hard
Correct Answer: changing direction of engines through 180°
Correct Answer: tubular section
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
