Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Railways See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Spacing of sleepers
Options- A. throughout the length of a rail is kept uniform
- B. near rail joints, is kept closer
- C. at the middle of rails, is kept closer
- D. none of these.
- Correct Answer
- at the middle of rails, is kept closer
- 1. Water paint is a
Options- A. white wash
- B. colour wash
- C. whiting
- D. distemper
- E. all the above. Discuss
- 2. Minimum depth of ballast prescribed of B.G. trunk lines of Indian Railways, is
Options- A. 20 cm
- B. 15 cm
- C. 25 cm
- D. 30 cm
- E. 35 cm Discuss
- 3. You are given a sample of soil containing coarse grains to determine its water content, you will use
Options- A. pycnometer
- B. oven-drying method
- C. calcium carbide method
- D. alcohol method. Discuss
- 4. Pick up the incorrect statement from the following :
Options- A. In radial flow, fluid flows such that pressure and velocity at any point change with respect to its distance from the central axis
- B. In radial flow, velocity of flow is in a radial direction
- C. In radial flow, flow may take place radially inward to or outward from the centre
- D. In radial flow, flow is one dimensional with stream lines parallel. Discuss
- 5. A fall which maintains its depth, is
Options- A. a trapezoidal notch fall
- B. a low weir fall
- C. a rectangular notch fall
- D. all the above. Discuss
- 6. Slump test is done for
Options- A. clay
- B. sand
- C. lime
- D. concrete. Discuss
- 7. Rankine-Golden formula accounts for direct as well as buckling stress and is applicable to
Options- A. very long columns
- B. long columns
- C. short columns
- D. intermediate columns
- E. all the above. Discuss
- 8. Design of highways is based on
Options- A. axle loads
- B. axle spacings
- C. wheel bases
- D. over all length
- E. all the above. Discuss
- 9. The ratio of the length of long chord and the tangent length of a circular curve of radius R deflecting through angle ?, is
Options- A. sin
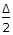
- B. cos
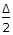
- C. tan
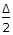
- D. 2 sin
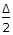
- E. 2 cos
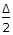 .
Discuss
.
Discuss
- 10. The ratio of maximum sewage flow to average sewage flow for mains up to 1 m in diameter, is
Options- A. 1.5
- B. 2.0
- C. 3.0
- D. 4.0 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: 25 cm
Correct Answer: pycnometer
Correct Answer: In radial flow, flow is one dimensional with stream lines parallel.
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: concrete.
Correct Answer: intermediate columns
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: 2 cos
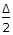 .
. Correct Answer: 2.0
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Advanced SurveyingAirport EngineeringApplied MechanicsBuilding ConstructionBuilding MaterialsConcrete TechnologyConstruction ManagementDocks and HarboursElements of Remote SensingEngineering EconomyEstimating and CostingGATE Exam QuestionsHighway EngineeringHydraulicsIrrigationRailwaysRCC Structures DesignSI UnitsSoil Mechanics and Foundation EngineeringSteel Structure DesignStrength of MaterialsStructural Design SpecificationsSurveyingTheory of StructuresTunnellingUPSC Civil Service Exam QuestionsWaste Water EngineeringWater Resources EngineeringWater Supply EngineeringProgramming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
