Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Railways See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
If w is width of sleepers, s is sleeper spacing and d is depth of ballast then
Options- A.
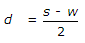
- B.
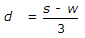
- C.
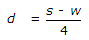
- D.
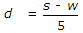
- E.
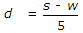
- Correct Answer
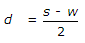
- 1. Total flow in stream is known
Options- A. run off
- B. stream flow
- C. discharge
- D. all the above. Discuss
- 2. Gravity conduits are generally in the form of
Options- A. canals
- B. flumes
- C. aqueduct
- D. tunnels
- E. all the above. Discuss
- 3. The tread of wheels is provided an outward slope of
Options- A. 1 in 10
- B. 1 in 15
- C. 1 in 20
- D. 1 in 25
- E. 1 in 30 Discuss
- 4. In SI units the power of sound is represented in
Options- A. kgs
- B. joules
- C. neutons
- D. watts. Discuss
- 5. Mostly used coagulant, is
Options- A. chlorine
- B. alum
- C. lime
- D. bleaching powder. Discuss
- 6. If the whole circle bearing of a line is 180°, its reduced bearing is
Options- A. S 0° E
- B. S 0° W
- C. S
- D. N. Discuss
- 7. A body of dimensions 1.5 m x 1.0 m x 2 m weighs 3000 kg in water. Its specific gravity is
Options- A. 0.8
- B. 0.9
- C. 1.0
- D. 1.1 Discuss
- 8. The maximum diameter of a bar used in a ribbed slab, is
Options- A. 12 mm
- B. 6 mm
- C. 20 mm
- D. 22 mm
- E. 24 mm Discuss
- 9. In plastic analysis, the shape factor for a circular section, is
Options- A. 1.5
- B. 1.6
- C. 1.7
- D. 1.75 Discuss
- 10. Meandering of a river generally occurs, in
Options- A. rocky stage
- B. delta stage
- C. boulder stage
- D. trough stage. Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: 1 in 20
Correct Answer: watts.
Correct Answer: alum
Correct Answer: S
Correct Answer: 1.1
Correct Answer: 22 mm
Correct Answer: 1.7
Correct Answer: trough stage.
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
