Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Railways See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The main advantage of a cement concrete sleeper, is :
Options- A. its heavy weight which improves the track modulus
- B. its capacity to maintain gauge
- C. its suitability for track circuiting
- D. its flat bottom which is very suitable for modern track
- E. all the above.
- Correct Answer
- all the above.
- 1. P is the force acting on a body whose mass is m and acceleration is f. The equation P - mf = 0, is known as
Options- A. equation of dynamics
- B. equation of dynamic equilibrium
- C. equation of statics
- D. none of these. Discuss
- 2. "All bodies at temperatures above absolute zero degree emit electromagnetic radiation at different wave length", is known as:
Options- A. Plank's law
- B. Planktan's law
- C. Lambert's cosine law
- D. None of these Discuss
- 3. Pick up the correct statement from the following:
Options- A. If the bed level is above N.S.L. the canal is called fully in baking and the berms are designed as 3 d where d is full supply depth of water (F.S.D.)
- B. Area of canal in cutting = BD + Sd2 where B = bed width, d = depth of cutting and S is the side slope
- C. Area of the bank of canal = B1d1 + Sd2 where B1, d1 and S are the width of bank, height of the bank above N.S.L. and side slope respectively
- D. If F.S.L. is above N.S.L the canal is called partly in cutting and partly in filling and berms are designed as 2d where d is full supply depth
- E. All the above. Discuss
- 4. For a given material, if E, C, K and m are Young's modulus, shearing modulus, bulk modulus and poisson ratio, the following relation does not hold good
Options- A.
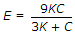
- B.
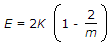
- C.
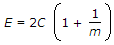
- D.
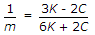
- E.
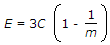 Discuss
Discuss
- 5. The breadth of a ribbed slab containing two bars must be between
Options- A. 6 cm to 7.5 cm
- B. 8 cm to 10 cm
- C. 10 cm to 12 cm
- D. 12 cm to 15 cm
- E. none of these. Discuss
- 6. The rocks which are formed due to cooling of magma at a relatively shallow depth from the earth's surface are called
Options- A. Plutonic rocks
- B. Hypabyssal rocks
- C. Volcanic rocks
- D. Ignoeous rocks. Discuss
- 7. The moment diagram for a cantilever carrying a concentrated load at its free end, will be
Options- A. triangle
- B. rectangle
- C. parabola
- D. cubic parabola. Discuss
- 8. Seasoning of timber is done for
Options- A. increasing moisture content
- B. decreasing moisture content
- C. increasing strength of timber
- D. none to these. Discuss
- 9. Raising of outer edge of a road with respect to inner edge, is known
Options- A. super elevation
- B. cant
- C. banking
- D. all the above. Discuss
- 10. Pick up the correct statement from the following:
Options- A. The refractive index of a medium varies according to the wavelength of the radiation,
- B. The variation of the refractive index with wave length, is called dispersion,
- C. The splitting of colours of white light by passing through a prism, is caused due to dispersion.
- D. All the these Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: equation of dynamics
Correct Answer: Plank's law
Correct Answer: All the above.
Correct Answer:
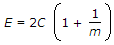
Correct Answer: 8 cm to 10 cm
Correct Answer: Hypabyssal rocks
Correct Answer: triangle
Correct Answer: decreasing moisture content
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: All the these
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
