Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Railways See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The place where a railway line and a road cross each other at the same level, is known as
Options- A. cross over
- B. railway junction
- C. road junction
- D. level crossing
- E. none of these.
- Correct Answer
- level crossing
- 1. Acid regression stage of sludge digestion at a temperature 21°C extends over a period of
Options- A. 15 days
- B. 30 days
- C. 60 days
- D. 90 days. Discuss
- 2. If the width of the foundation for two equal columns is restricted, the shape of the footing generally adopted, is
Options- A. square
- B. rectangular
- C. trapezoidal
- D. triangular. Discuss
- 3. At eastern elongation, the pole star moves
Options- A. eastward
- B. westward
- C. northward
- D. southward. Discuss
- 4. For loss of head in a canal inverted syphon barrel, the factor in the Unwin formula
 is a coefficient for loss of head due to
is a coefficient for loss of head due to
Options- A. friction
- B. exit
- C. entry
- D. gradient Discuss
- 5. The force in AD of the truss shown in given figure, is
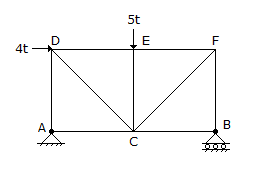
Options- A. 4.0t compression
- B. 3.0t compression
- C. 0.5t compression
- D. 0.5t tension
- E. zero. Discuss
- 6. Rapid curing cut back bitumen is produced by blending bitumen with
Options- A. Kerosene
- B. Benzene
- C. Diesel
- D. Petrol Discuss
- 7. Fresh sewage is generally
Options- A. alkaline
- B. acidic
- C. highly decomposed
- D. a source of objectionable odour. Discuss
- 8. The coefficient ka of the active earth pressure, is given by
Options- A.

- B.

- C.

- D.
 Discuss
Discuss
- 9. Pick up the correct statement from the following:
Options- A. The diameter of a rivet, before driving is taken as the nominal diameter of the rivet
- B. The diameter of the rivet hole is taken as the gross area of the rivet
- C. For rivets of nominal diameters less than 25 mm, the diameter of the rivet hole is taken as the nominal diameter of the rivet plus 1.5 mm
- D. For rivets of nominal diameters exceeding 25 mm, the diameter of the rivet hole is taken as the nominal diameter of the rivet plus 2 mm
- E. All the above. Discuss
- 10. Ratio of bearing capacity of double Under Reamed (U.R.) pile to that of single U.R. pile is nearly
Options- A. 2
- B. 1.5
- C. 1.2
- D. 1.7 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 90 days.
Correct Answer: rectangular
Correct Answer: northward
Correct Answer: entry
Correct Answer: 0.5t compression
Correct Answer: Petrol
Correct Answer: alkaline
Correct Answer:

Correct Answer: All the above.
Correct Answer: 1.5
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
