Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Irrigation See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
In a barrage, the crest level is kept
Options- A. low with large gates
- B. high with large gates
- C. high with no gates
- D. low with no gates.
- Correct Answer
- low with large gates
- 1. If the width of a simply supported beam carrying an isolated load at its centre is doubled, the deflection of the beam at the centre is changed by
Options- A. 1/2
- B. 1/8
- C. 2
- D. 8
- E. 4 Discuss
- 2. Electromagnetic spectrum contains :
Options- A. gamma rays (wave length < 10-10 m)
- B. ultraviolet rays (wave length < 10-6 m)
- C. infrared rays (wave length < 10-4 m)
- D. radio rays (wave length > 1 m)
- E. All of these Discuss
- 3. The diaphragm of a stadia theodolite is fitted with two additional
Options- A. horizontal hairs
- B. vertical hairs
- C. horizontal and two vertical hairs
- D. none of these. Discuss
- 4. Modified moment of inertia of sections with a single web, is equal to moment of inertia of the section about Y-Y axis at the point of maximum bending moment and is multiplied by the ratio of
Options- A. area of compression flange at the minimum bending moment to the corresponding area at the point of maximum bending moment
- B. area of tension flange at the minimum bending moment of the corresponding area at the point of maximum bending moment
- C. total area of flanges at the maximum bending moment to the corresponding area at the point of maximum bending moment
- D. none of these. Discuss
- 5. Pick up the correct statement from the following:
Options- A. Runway edge from the landing side, is called threshold
- B. Localizer indicates to the pilot his position with respect to the proposed alignment
- C. The glide slope indicates the correct angle of descent
- D. L.O.M. and L.M.M. help the pilot to judge his position for the runway
- E. All the above. Discuss
- 6. The maximum energy stored at elastic limit of a material is called
Options- A. resilience
- B. proof resilience
- C. modulus of resilience
- D. bulk resilience Discuss
- 7. The ratio of frictional factor and coefficient of friction used in general equation for a head loss in a pipe, is
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 8. An aggregate is known as cyclopean aggregate if its size is more than
Options- A. 4.75 mm
- B. 30 mm
- C. 60 mm
- D. 75 mm
- E. 90 mm. Discuss
- 9. Pick up the correct statement from the following
Options- A. Approach of the water line in a flumed channel section should not be steeper than
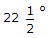
- B. Departure of the water line from a flumed channel section should not be steeper than 30°
- C. Approach of the water line should not be steeper than 30° and departure line not steeper than
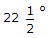 in a flumed channel section
in a flumed channel section - D. Approach and departure of the water line in a flumed channel section, should not be steeper than
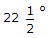 Discuss
Discuss
- 10. Minimum permissible speed on high speed roads, is decided on the basis of
Options- A. 15 percentile cumulative frequency
- B. 20 percentile cumulative frequency
- C. 30 percentile cumulative frequency
- D. 40 percentile cumulative frequency. Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 1/2
Correct Answer: All of these
Correct Answer: horizontal hairs
Correct Answer: total area of flanges at the maximum bending moment to the corresponding area at the point of maximum bending moment
Correct Answer: All the above.
Correct Answer: proof resilience
Correct Answer: 4
Correct Answer: 75 mm
Correct Answer: Approach of the water line should not be steeper than 30° and departure line not steeper than
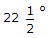 in a flumed channel section
in a flumed channel section Correct Answer: 15 percentile cumulative frequency
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
