Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The shear strength in plastic undrained clay, is due to
Options- A. inter-granular friction
- B. internal friction
- C. cohesion
- D. none of these.
- Correct Answer
- cohesion
- 1. Kinetic friction may be defined as
Options- A. friction force acting when the body is just about to move
- B. friction force acting when the body is in motion
- C. angle between normal reaction and resultant of normal reaction and limiting friction
- D. ratio of limiting friction and normal reaction. Discuss
- 2. A scissors cross-over consists of
Options- A. two pairs of points, four acute angle crossings and two obtuse angle crossings
- B. four pairs of points, four acute angle crossings and four obtuse angle crossings
- C. four pairs of points, six acute angle crossings and two obtuse angle crossings
- D. two pairs of points, six acute angle crossings and four obtuse angle crossings. Discuss
- 3. The Mohr's straight theory is based on the following fact :
Options- A. Material fails essentially by shear
- B. Ultimate strength of the material is determined by the stress in the plane of slip
- C. Failure criterion is independent of the intermediate principal stress
- D. All the above. Discuss
- 4. If a column is subjected to dead load and super imposed load only, the maximum ratio
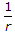 should not be greater than
should not be greater than
Options- A. 180
- B. 250
- C. 350
- D. 400 Discuss
- 5. Maximum strain theory for the failure of a material at the elastic limit, is known as
Options- A. Guest's or Trecas' theory
- B. St. Venant's theory
- C. Rankine's theory
- D. Haig's theory
- E. Von Mises's theory. Discuss
- 6. Snow consists of
Options- A. snow crystals
- B. rimed snow crystals
- C. snow flakes
- D. All of these Discuss
- 7. Pick up the correct statement from the following:
Options- A. Styrene resin is produced from ethylene which is made from petroleum
- B. Styrene resin is light in weight
- C. Styrene resin transmits ultraviolet waves of light
- D. Styrene resin is used to manufacture utensils which are unaffected by chemicals
- E. All the above. Discuss
- 8. The minimum head room over a stair must be
Options- A. 200 cm
- B. 205 cm
- C. 210 cm
- D. 200 cm
- E. 230 cm Discuss
- 9. Number of links per metre length of a chain are
Options- A. 2
- B. 5
- C. 8
- D. 10
- E. 20 Discuss
- 10. Stainless steel resists corrosion due to
Options- A. carbon
- B. sulphur
- C. vanadium
- D. chromium
- E. maganese. Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: friction force acting when the body is in motion
Correct Answer: four pairs of points, six acute angle crossings and two obtuse angle crossings
Correct Answer: All the above.
Correct Answer: 180
Correct Answer: St. Venant's theory
Correct Answer: All of these
Correct Answer: All the above.
Correct Answer: 210 cm
Correct Answer: 5
Correct Answer: chromium
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
