Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
An infinite slope is inclined at angle i and has its angle of internal friction ?, the stability number Sa, is
Options- A.
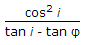
- B.
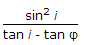
- C. (tan i - tan ?) cos2 i
- D. (tan i - tan ?) sin2 i
- Correct Answer
- (tan i - tan ?) cos2 i
- 1. The coefficient of curvature for a well graded soil, must be between
Options- A. 0.5 to 1.0
- B. 1.0 to 3.0
- C. 3.0 to 4.0
- D. 4.0 to 5.0 Discuss
- 2. Due to attack of dry rot, the timber
Options- A. cracks
- B. shrinks
- C. reduces to powder
- D. none of these. Discuss
- 3. In reciprocal levelling, the error which is not completely eliminated, is due to
Options- A. earth's curvature
- B. non-adjustment of line of collimation
- C. refraction
- D. non-adjustment of the bubble tube. Discuss
- 4. Water cement ratio is generally expressed in volume of water required per
Options- A. 10 kg
- B. 20 kg
- C. 30 kg
- D. 40 kg
- E. 50 kg Discuss
- 5. The side of a rail diamond may be obtained by dividing the gauge of track by
Options- A. sine of acute crossing
- B. consine of acute crossing
- C. tangent of acute crossing
- D. cotangent of acute crossing. Discuss
- 6. As per I.S. 456 - 1978, the pH value of water shall be
Options- A. less than 6
- B. equal to 6
- C. not less than 6
- D. equal to 7 Discuss
- 7. The declination and right ascension of the sun are each equal to zero on
Options- A. March 21
- B. June 21
- C. September 21
- D. December 22. Discuss
- 8. A compound truss may be formed by connecting two simple rigid frames, by
Options- A. two bars
- B. three bars
- C. three parallel bars
- D. three bars intersecting at a point. Discuss
- 9. Arrangement made to divert the trains from one track to another, is known as
Options- A. railway point
- B. railway crossing
- C. turnout
- D. railway junction
- E. none of these. Discuss
- 10. The ratio of the stresses produced by a suddenly applied load and by a gradually applied load on a bar, is
Options- A.
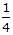
- B.
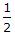
- C. 1
- D. 2
- E. 3 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 1.0 to 3.0
Correct Answer: reduces to powder
Correct Answer: refraction
Correct Answer: 50 kg
Correct Answer: sine of acute crossing
Correct Answer: not less than 6
Correct Answer: March 21
Correct Answer: three bars
Correct Answer: turnout
Correct Answer: 2
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
