Discussion
Home ‣ Logical Reasoning ‣ Logical Deduction See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Statements: All needles are threads. All threads are boxes. All trees are boxes.
Conclusions:
- No needle is tree.
- Some trees are threads.
- Some boxes are needles.
- Some trees are needles.
Options- A. None follows
- B. Only either I or IV follows
- C. Only either I or IV, and II follow
- D. Only III follows
- E. Only either I or IV, and III follow
- Correct Answer
- Only either I or IV, and III follow
ExplanationAll needles are threads. All threads are boxes.Since both the premises are universal and affirmative, the conclusion must be universal affirmative (A-type) and should not contain the middle term. So, it follows that 'All needles are boxes'. III is the converse of this conclusion and so it holds.
All threads are boxes. All trees are boxes.
Since the middle term 'boxes' is not distributed even once in the premises, no definite conclusion follows.
All needles are boxes. All trees are boxes.
Again, since the middle term 'boxes' is not distributed even once in the premises, no definite conclusion can be drawn. However, I and IV involve the extreme terms of these two statements and form a complementary pair. Thus, either I or IV follows.
More questions
- 1. Statement: Many historians have done more harm than good by distorting truth.
Assumptions:
- People believe what is reported by the historians.
- Historians are seldom expected to depict the truth.
Options- A. Only assumption I is implicit
- B. Only assumption II is implicit
- C. Either I or II is implicit
- D. Neither I nor II is implicit
- E. Both I and II are implicit Discuss
Correct Answer: Only assumption I is implicit
Explanation:
The fact that historians have done harm by distorting truth, means that people believe what is reported by the historians. So, I is implicit. II does not follow from the statement and so is not implicit.- 2. Look at this series: 58, 52, 46, 40, 34, ... What number should come next?
Options- A. 26
- B. 28
- C. 30
- D. 32 Discuss
Correct Answer: 28
Explanation:
This is a simple subtraction series. Each number is 6 less than the previous number.- 3. Which word does NOT belong with the others?
Options- A. tape
- B. twine
- C. cord
- D. yarn Discuss
Correct Answer: tape
Explanation:
The yarn, twine, and cord are all used for tying. The tape is not used in the same way.- 4. Choose the picture that would go in the empty box so that the two bottom pictures are related in the same way as the top two:
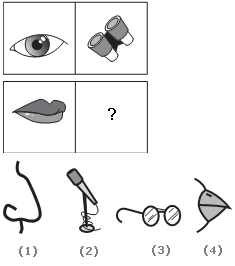
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
Correct Answer: 2
Explanation:
An eye is to a pair of binoculars as a mouth is to a microphone. This relationship shows magnification. The binoculars help one see farther. The microphone helps one speak louder.- 5. A Guarantee is a promise or assurance that attests to the quality of a product that is either (1) given in writing by the manufacturer or (2) given verbally by the person selling the product. Which situation below is the best example of a Guarantee?
Options- A. Melissa purchases a DVD player with the highest consumer ratings in its category.
- B. The salesperson advises Curt to be sure that he buys an air conditioner with a guarantee.
- C. The local auto body shop specializes in refurbishing and selling used cars.
- D. Lori buys a used digital camera from her coworker who says that she will refund Lori's money if the camera's performance is not of the highest quality. Discuss
Correct Answer: Lori buys a used digital camera from her coworker who says that she will refund Lori's money if the camera's performance is not of the highest quality.
Explanation:
Choices a, b, and c do not describe situations in which a product is guaranteed. Only choice d reflects a situation in which a seller attests to the quality of a product by giving the buyer a promise or assurance about its quality.- 6. B2CD, _____, BCD4, B5CD, BC6D
Options- A. B2C2D
- B. BC3D
- C. B2C3D
- D. BCD7 Discuss
Correct Answer: BC3D
Explanation:
Because the letters are the same, concentrate on the number series, which is a simple 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 series, and follows each letter in order.- 7. Statement: "You should not grant him leave in this week due to exigency of work." - A supervisor advises the administrative officer.
Assumptions:
- Request for leave can be turned down also.
- The supervisor has reviewed the work required to be done during the said period.
Options- A. Only assumption I is implicit
- B. Only assumption II is implicit
- C. Either I or II is implicit
- D. Neither I nor II is implicit
- E. Both I and II are implicit Discuss
Correct Answer: Both I and II are implicit
Explanation:
The advice is given to turn down the request for leave. So, I is implicit. The mention of the 'exigency of work' makes II implicit.- 8. Statements: In a one day cricket match, the total runs made by a team were 200. Out of these 160 runs were made by spinners.
Conclusions:
- 80% of the team consists of spinners.
- The opening batsmen were spinners.
Options- A. Only conclusion I follows
- B. Only conclusion II follows
- C. Either I or II follows
- D. Neither I nor II follows
- E. Both I and II follow Discuss
Correct Answer: Neither I nor II follows
Explanation:
According to the statement, 80% of the total runs were made by spinners. So, I does not follow. Nothing about the opening batsmen is mentioned in the statement. So, II also does not follow.- 9. Statement: "This drink can be had either as it is, or after adding ice to it." - An advertisement.
Assumptions:
- People differ in their preferences.
- Some people will get attracted to the drink as it can be had as it is.
Options- A. Only assumption I is implicit
- B. Only assumption II is implicit
- C. Either I or II is implicit
- D. Neither I nor II is implicit
- E. Both I and II are implicit Discuss
Correct Answer: Both I and II are implicit
Explanation:
The advertisement tells the different ways in which the drink can be had. This means that different people prefer to have it in a different way and that some people would prefer it only because it can be taken in a particular manner. So, both I and II are implicit.- 10. Statements: Some trains are roads. No road is jungle. All flowers are jungles.
Conclusions:
- Some trains are flowers.
- Some trains are jungles.
- Some flowers are trains.
- No road is flower.
Options- A. None follows
- B. Only II follows
- C. Only III follows
- D. Only IV follows
- E. All follow Discuss
Correct Answer: Only IV follows
Explanation:
Some trains are roads. No road is jungle.Since one premise is particular and the other negative, the conclusion must be particular negative and should not contain the middle term. So, it follows that 'Some trains are not jungles'.
No road is jungle. All flowers are jungles.
Since both the premises are universal and one premise is negative, the conclusion must be universal negative and should not contain the middle term. So, it follows that 'No flower is road'. IV is the converse of this conclusion and so it holds.
Some trains are roads, No flower is road.
As discussed above, it follows that 'Some trains are not flowers'.
Comments
There are no comments.
- 1. Statement: Many historians have done more harm than good by distorting truth.
More in Logical Reasoning:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
