Discussion
Home ‣ Electrical Engineering ‣ Time Response of Reactive Circuits Comments
- Question
When a 24 V input pulse with a width equal to five time constants is applied to an RC integrator, the capacitor charges to
Options- A. 24 V
- B. 15.12 V
- C. 20.64 V
- D. 12 V
- Correct Answer
- 24 V
- 1. In an RL differentiator, when the input pulse goes from its low level to its high level,
Options- A. the inductor prevents a sudden change in voltage
- B. the inductor prevents a sudden change in current
- C. voltage across the inductor instantly reaches 63% of input voltage
- D. voltage across the inductor is zero Discuss
- 2. A steady-state condition is reached when
Options- A. the output voltage reaches the average value of the input voltage
- B. the output voltage reaches the input voltage
- C. the output voltage reaches approximately 63% of the input voltage
- D. the output voltage reaches the effective value of the input voltage Discuss
- 3. In an RC differentiator, the sum of the capacitor voltage and the resistor voltage at any instant
Options- A. must be zero
- B. must be equal to the applied voltage
- C. is less than the applied voltage but greater than zero
- D. cannot be determined Discuss
- 4. In an RC differentiator, the capacitor
Options- A. charges exponentially at a rate depending on the RC time constant
- B. charges exponentially at a rate depending on the input voltage
- C. charges when the input voltage is decreasing
- D. charges to approximately one time constant Discuss
- 5. If the RC time constant of an integrator is increased, as the time constant is increased
Options- A. the capacitor charges more during a pulse and discharges less between pulses
- B. the capacitor charges less during a pulse and discharges more between pulses
- C. the capacitor charges more during a pulse and discharges more between pulses
- D. the capacitor charges less during a pulse and discharges less between pulses Discuss
- 6. To understand how the output voltage is shaped by a differentiator, you must consider
Options- A. the response to the rising pulse edge
- B. the response between the rising and falling edges
- C. the response to the falling pulse edge
- D. all of the above Discuss
- 7. Referring this figure, on the falling edge,
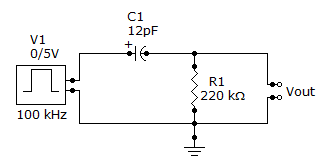
Options- A. the resistor voltage drops to ?5 V and then goes back to zero exponentially
- B. the resistor voltage jumps to ?5 V and then goes back to zero exponentially
- C. the capacitor voltage remains constant
- D. the resistor voltage jumps to +5 V and then decreases exponentially to zero Discuss
- 8. Referring to Problem 5, how long will it take the capacitor to discharge if the internal resistance of the pulse source is 100 Ω?
Options- A. 300 µs
- B. 600 µs
- C. 900 µs
- D. 1.5 ms Discuss
- 9. When a 15 V input pulse with a width equal to two time constants is applied to an RC integrator, the capacitor charges to
Options- A. 15 V
- B. 12.9 V
- C. 8.6 V
- D. 19.45 V Discuss
- 10. Referring to the above figure, determine the voltage level that the output will reach during the pulse.
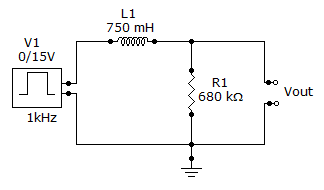
Options- A. 0 V
- B. 15 V
- C. 6.3 V
- D. 9.45 V Discuss
Time Response of Reactive Circuits problems
Search Results
Correct Answer: the inductor prevents a sudden change in current
Correct Answer: the output voltage reaches the average value of the input voltage
Correct Answer: must be equal to the applied voltage
Correct Answer: charges exponentially at a rate depending on the RC time constant
Correct Answer: the capacitor charges less during a pulse and discharges less between pulses
Correct Answer: all of the above
Correct Answer: the resistor voltage jumps to ?5 V and then goes back to zero exponentially
Correct Answer: 1.5 ms
Correct Answer: 12.9 V
Correct Answer: 9.45 V
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electrical Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
