Discussion
Home ‣ Electrical Engineering ‣ Circuit Theorems in AC Analysis See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Referring to the given circuit, what is ZTH if R1 is changed to 220 Ω?
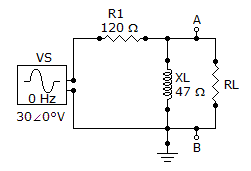
Options- A. 225∠12.1° Ω
- B. 225∠77.9° Ω
- C. 46∠77.9° Ω
- D. 46∠12.1° Ω
- Correct Answer
- 46∠77.9° Ω
- 1. Referring to Problem 15, if the input voltage is a 6 V sine wave with a dc level of 10 V, what is the output voltage magnitude?
Options- A. 6 V
- B. 597 mV
- C. 5.97 V
- D. 0 V Discuss
- 2. The minimum resistance value for a blue, gray, red, silver resistor is
Options- A. 612 Ω
- B. 6,120 Ω
- C. 6,800 Ω
- D. 6,460 Ω Discuss
- 3. Four 8 Ω speakers are connected in parallel to the output of an audio amplifier. If the maximum voltage to the speakers is 12 V, the amplifier must be able to deliver to the speakers
Options- A. 18 W
- B. 1.5 W
- C. 48 W
- D. 72 W Discuss
- 4. Referring to circuit given, if R1 is changed to a 68 Ω resistor, what will be the current through it?

Options- A. 0.16 A
- B. 0.24 A
- C. 0.2 A
- D. 0.04 A Discuss
- 5. The induced voltage across a coil with 250 turns that is located in a magnetic field that is changing at a rate of 8 Wb/s is
Options- A. 1,000 V
- B. 2,000 V
- C. 31.25 V
- D. 3,125 V Discuss
- 6. A 10 Ω resistor, a 90 mH coil, and a 0.015 µF capacitor are in series across an ac source. The impedance magnitude at 1,200 Hz below fr is
Options- A. 1,616 Ω
- B. 161 Ω
- C. 3,387 Ω
- D. 1,771 Ω Discuss
- 7. Approximately how much current flows through a 3.3 MΩ resistor across a 30 V source?
Options- A. 9 µA
- B. 90 µA
- C. 900 µA
- D. 9000 µA Discuss
- 8. In a certain transformer, the input power to the primary is 120 W. If 8.5 W are lost to the winding resistance, what is the output power to the load, neglecting any other issues?
Options- A. 0 W
- B. 14.1 W
- C. 111.5 W
- D. 1,020 W Discuss
- 9. A balanced load is one in which all the impedances are equal.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. A 470 Ω resistor, a 220 Ω resistor, and a 100 Ω resistor are all in parallel. The total resistance is approximately
Options- A. 790 Ω
- B. 470 Ω
- C. 60 Ω
- D. 30 Ω Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 5.97 V
Correct Answer: 6,120 Ω
Explanation:
Because of 10% tolerance(last color silver), this resistance may vary 10% of 6800.
Minimum resistance value = 6800 - 680 = 6120
Maximum resistance value = 6800 + 680 = 7480
Correct Answer: 72 W
Correct Answer: 0.16 A
Correct Answer: 2,000 V
Correct Answer: 1,616 Ω
Correct Answer: 9 µA
Correct Answer: 111.5 W
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: 60 Ω
Explanation:
1/R = (1/470 + 1/220 + 1/100)
R = 59.98 ohm
R = 59.98 ohm
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electrical Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
