Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics and Communication Engineering ‣ Matching Questions See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Match the following:
List I (Oscillator) List II (Features) A. Wien Bridge 1. RF oscillator, uses two inductors and one capacitor B. Colpitt's 2. LC oscillator for radio frequencies uses three capacitances and one inductance C. Hartley 3. RC oscillator for audio frequencies D. Clapp 4. RF oscillator, uses two capacitances and one inductance
Options- A. A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
- B. A-2, B-4, C-1, D-3
- C. A-3, B-4, C-1, D-2
- D. A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
- Correct Answer
- A-3, B-4, C-1, D-2
- 1. As compared to dimensions of most feeds, the skin depth at microwave frequencies is
Options- A. of the same magnitude
- B. much larger
- C. much smaller
- D. either (b) or (c) Discuss
- 2. For a 1 cm x 2 cm air filled rectangular waveguide the maximum frequency should be less than about
Options- A. 1000 MHz
- B. 5000 MHz
- C. 14000 MHz
- D. 140000 MHz Discuss
- 3. In a radio receiver
Options- A. all stages contribute equally to noise
- B. RF stage has no effect on S/N ratio
- C. mixer stage contributes most of the noise generated Discuss
- 4. As compared to an ordinary semiconductor diode, a Schottky diode
Options- A. has higher reverse saturation current
- B. has higher reverse saturation current and higher cut in voltage
- C. has higher reverse saturation current and lower cut in voltage
- D. has lower reverse saturation current and lower cut in voltage Discuss
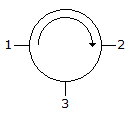
- 5. A 3 port circulator is in the given figure. Its scattering matrix is
Options- A.
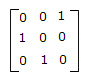
- B.
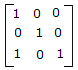
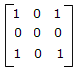
- C.
- D.
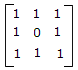 Discuss
Discuss
- 6. The total field developed by an antenna array at a distant point is
Options- A. phasor sum of fields produced by individual antennas of the array
- B. algebraic sum of fields produced by individual antennas of the array
- C. either (a) or (b) depending on type of array
- D. neither (a) nor (b) Discuss
- 7. A standard cell of 1.0185 V is used with a slide wire potentiometer. The balance was obtained at 60 cm. When an unknown emf was connected, the balance was obtained at 82 cm. The magnitude of unknown emf is
Options- A. 1.39 V
- B. 0.75 V
- C. 13.9 V
- D. 7.45 V Discuss
- 8. The number of valence electrons in donor impurity are
Options- A. 5
- B. 4
- C. 3
- D. 1 Discuss
- 9. Assertion (A): A DIAC has four layers but only two terminals.
Reason (R): A DIAC can conduct in both directions.
Options- A. Both A and R are correct and R is correct explanation of A
- B. Both A and R correct but R is not correct explanation of A
- C. A is correct but R is wrong
- D. A is wrong but R is correct Discuss
- 10. A NAND gate has 3 inputs and one output. The number of thyristors required for this gate are
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 3 or 4 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: of the same magnitude
Correct Answer: 14000 MHz
Correct Answer: mixer stage contributes most of the noise generated
Correct Answer: has higher reverse saturation current and lower cut in voltage
Explanation:
This is due to high electron concentration in metals.
Correct Answer:
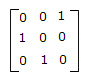
Correct Answer: phasor sum of fields produced by individual antennas of the array
Explanation:
Since field is a phasor quantity we have to take phasor sum.
Correct Answer: 1.39 V
Explanation:
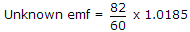 .
.
Correct Answer: 5
Explanation:
Donor impurity has 5 valence electrons (while silicon has 4 valence electrons).
Hence donor impurity can donate electrons.
Correct Answer: Both A and R correct but R is not correct explanation of A
Correct Answer: 3
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
