Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics and Communication Engineering ‣ Matching Questions See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Match the following:
List I List II A. 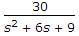
1. Zero B. 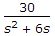
2. 0.2 C. 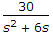
3. Actuator D. 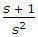
4. infinity
Options- A. A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
- B. A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
- C. A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
- D. A-4, B-2, C-3, D-1
- Correct Answer
- A-4, B-2, C-3, D-1
- 1. Resistivity of metals consists of two parts, one part constant and the other temperature dependent.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 2. The given figure shows a pole zero diagram. The transfer function G(j1) is
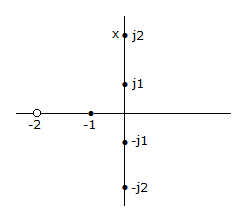
Options- A. 0.5 ?0
- B. 2.7 ?- 31°
- C. 2 ?45°
- D. 2 ?- 67.4° Discuss
- 3. The total number of leads in SUS, SBS and SCS respectively are
Options- A. 3, 3, 4,
- B. 3, 3, 3
- C. 2, 3, 3
- D. 3, 3, 5 Discuss
- 4. Assertion (A): Free space does not interfere with normal radiation and propagation of radio waves
Reason (R): Free space has no magnetic or gravitational fields.
Options- A. Both A and R are correct and R is correct explanation of A
- B. Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A
- C. A is correct but R is wrong
- D. A is wrong but R is correct Discuss
- 5. Assertion (A): The angular momentum of an atom is due to three contributions viz. orbital, electron spin and nuclear spin.
Reason (R): The nuclear spin magnetic moment is much more than electron spin magnetic moment.
Options- A. Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A
- B. Both A and R are true but R is not correct explanation of A
- C. A is true but R is false
- D. A is false but R is true Discuss
- 6. Match the following:
List I (Octal) List II (Hexadecimal) A. 66 1. 3 F B. 77 2. 36 C. 55 3. 27 D. 47 4. 3D
Options- A. A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
- B. A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
- C. A-3, B-1, C-2, D-4
- D. A-4, B-1, C-2, D-3 Discuss
- 7. The relationship of hysteresis loss to maximum flux density was first determined by
Options- A. C. Steinmetz
- B. G.R. Kirchoff
- C. Mr. Laplace
- D. Mr. Ampere Discuss
- 8. Oscillations are obtained from a reflex klystron only for combinations of anode voltage and repeller voltage that give a favourable transit time.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 9. The duty cycle of a step down chopper is
Options- A.
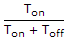
- B.
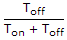
- C.
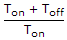
- D.
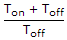 Discuss
Discuss
- 10. The use of free wheeling diode in controlled rectifier improves the waveshape of load current.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: 0.5 ?0
Explanation:
Join j1 point with the zero and poles. Find magnitude and phase angles of all these lines.
Correct Answer: 3, 3, 4,
Correct Answer: Both A and R are correct and R is correct explanation of A
Explanation:
Since free space does not have magnetic and other fields, waves can propagate without any interference.
Correct Answer: A is true but R is false
Explanation:
Nuclear spin is of the same order as electron sum.
Correct Answer: A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
Correct Answer: C. Steinmetz
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer:
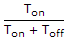
Correct Answer: True
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
