Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics and Communication Engineering ‣ Power Electronics See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
A thyristor has a turn on time of 6 ?s. If the anode circuit is inductive, the turn on time will be
Options- A. 6 ?s
- B. less than 6?s
- C. more than 6 ?s
- D. either 6 ?s or less
- Correct Answer
- more than 6 ?s
ExplanationInductive load increases the turn on time.
More questions
- 1. The power requirements of a DRAM in active and stand by modes is about
Options- A. 350 mW and 5 mW respectively
- B. 350 mW each
- C. 5 mW each
- D. 350 mW and 100 mW respectively Discuss
Correct Answer: 350 mW and 5 mW respectively
Explanation:
Power requirement in stand by mode is very low 1000.- 2. The different access methods which permit many satellite users to operate in parallel through a single transponder without interfering with each other as
Options- A. Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA)
- B. Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA)
- C. Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
- D. All of the above Discuss
Correct Answer: All of the above
- 3. Match the following:
List I List II A. T (Reflection coefficient) = 0 1. (ZL - Zo)/(ZL + Zo) B. T = - 1 2. ZL = Zo C. T = + 1 3. ZL = 0 D. - 1 < T < + 1 4. ZL = ?
Options- A. A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
- B. A-2, B-4, C-1, D-3
- C. A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
- D. A-3, B-2, C-4, D-1 Discuss
Correct Answer: A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
- 4. Assertion (A): Ferromagnetic materials possess ferromagnetic properties only when temperature is less than paramagnetic curie temperature.
Reason (R): For a ferromagnetic material
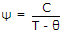 for T > ?f.
for T > ?f.
Options- A. Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A
- B. Both A and R are true but R is not correct explanation of A
- C. A is true but R is false
- D. A is false but R is true Discuss
Correct Answer: Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A
- 5. Bode magnitude plot is drawn between
Options- A. magnitude of network function and ?
- B. dB magnitude and log ?
- C. dB magnitude and ?
- D. loge (magnitude) and log ? Discuss
Correct Answer: dB magnitude and log ?
Explanation:
Frequency is plotted on log scale and magnitude is taken in dB.- 6. A two branch parallel circuit has a 20 ? resistance and 1 H inductance in one branch and a 100 ?F capacitor in the second branch. It is fed from 100 V ac supply, at resonance, the input impedance of the circuit is
Options- A. 500 ?
- B. 50 ?
- C. 20 ?
- D. 5 ? Discuss
Correct Answer: 500 ?
Explanation:
At parallel resonance circuit impedance =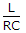 .
.
- 7. The temperature coefficient of a thermistor
Options- A. is positive
- B. is negative
- C. zero
- D. may be positive or negative depending on its composition Discuss
Correct Answer: is negative
- 8. An amplifier has a large ac input signal. The clipping occurs on both the peaks. The output voltage will be nearly a
Options- A. sine wave
- B. square wave
- C. triangular wave
- D. (a) or (c) Discuss
Correct Answer: square wave
Explanation:
When a sinusoidal voltage is clipped on both sides it resembles a square wave.- 9. In the figure shown, A1, A2, A3 are identical Ammeters. If A1 and A3 read 5 and 13 A respectively, reading of A2 will be
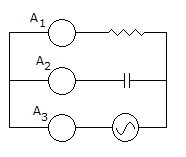
Options- A. 8
- B. 13 A
- C. 18
- D. 12 A Discuss
Correct Answer: 12 A
Explanation:
A2 = 132 - 25 ⟹ 12 A.- 10. A relaxation oscillator uses
Options- A. tunnel diode
- B. UJT
- C. both tunnel diode and UJT
- D. PIN diode Discuss
Correct Answer: UJT
Comments
There are no comments.
More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
