Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics and Communication Engineering ‣ Satellite Communication See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Radio broadcasting is a familiar example of
Options- A. space multiplexing
- B. time multiplexing
- C. frequency multiplexing
- D. none of the above
- Correct Answer
- frequency multiplexing
- 1. If an amplifier with gain of - 1000 and feedback factor ? = - 0.1 had a gain change of 20% due to temperature, the change in gain of the feedback amplifier would be
Options- A. 10%
- B. 5%
- C. 0.2%
- D. 0.01% Discuss
- 2. Permeability is analogous to
Options- A. resistivity
- B. retentivity
- C. conductivity
- D. coercivity Discuss
- 3. In a Gunn diode oscillator drift velocity of electron is 107 cm/s and active region length is 10 x 10-4 cm. The natural frequency of oscillation is
Options- A. 1 MHz
- B. 10 MHz
- C. 1 GHz
- D. 10 GHz Discuss
- 4. A cycloconverter is a group of controlled rectifiers.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 5. If the valence electron is separated from a copper atom, the remaining part of atom has a net charge of
Options- A. 1
- B. - 1
- C. 0
- D. + 3 Discuss
- 6. A single phase bridge type cycloconverter uses eight thyristors.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 7. ?r is determined by the atomic structure of the dielectric.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 8. An SBS can conduct is one direction only.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 9. The resistivity of intrinsic semiconductors, at room temperature, is of the order of
Options- A. 1 ?-m
- B. 1000 ?-m
- C. 106 ?-m
- D. 10-3 ?-m Discuss
- 10. The orientation polarization of a polyatomic gas is inversely proportional to absolute temperature.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 0.2%
Explanation:
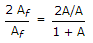
As we know, Gain with feedback
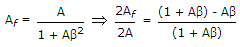
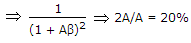
A = - 1000, ? = -0.1 .
Correct Answer: conductivity
Correct Answer: 10 GHz
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: 1
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Explanation:
It is a bilateral switch.
Correct Answer: 1 ?-m
Correct Answer: True
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Analog ElectronicsAutomatic Control SystemsCommunication SystemsDigital ElectronicsElectromagnetic Field TheoryElectronic Devices and CircuitsExam Questions PapersMatching QuestionsMaterials and ComponentsMeasurements and InstrumentationMicroprocessorsMicrowave CommunicationNetworks Analysis and SynthesisPower ElectronicsRadio ReceiversSatellite CommunicationSignals and SystemsProgramming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
