Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics and Communication Engineering ‣ Radio Receivers See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
If the intermediate frequency of a superheterodyne receiver falls within the tuning range of the receiver
Options- A. Unsuitability will occur
- B. Heterodyne whistles will be heard
- C. Tuning to the frequency band immediately adjacent to the intermediate frequency will become impossible
- D. All of the above
- Correct Answer
- All of the above
- 1. In pulse width modulation of chopper
Options- A. T is kept constant and Ton is varied
- B. Ton is kept constant T is varied
- C. both T and Ton are varied
- D. either T or Ton is varied Discuss
- 2. The colour code on a carbon resistor is green-blue-yellow. The tolerance is
Options- A. ± 5%
- B. ± 10%
- C. ± 20%
- D. ± 30% Discuss
- 3. Wave guides are pressurised above normal atmospheric pressure for
Options- A. increasing the power handling capacity
- B. improving conductivity of walls
- C. preventing higher modes from propagation
- D. varying the wave impedance Discuss
- 4. A transmission line discontinuity is defined as any interruption in the uniformity of the line.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 5. Which of the following is not a valid variable name in C?
Options- A. 1 a
- B. a 1 2
- C. a b 123
- D. a b c 123 Discuss
- 6. If an amplifier with gain of - 1000 and feedback factor ? = - 0.1 had a gain change of 20% due to temperature, the change in gain of the feedback amplifier would be
Options- A. 10%
- B. 5%
- C. 0.2%
- D. 0.01% Discuss
- 7. Permeability is analogous to
Options- A. resistivity
- B. retentivity
- C. conductivity
- D. coercivity Discuss
- 8. In a Gunn diode oscillator drift velocity of electron is 107 cm/s and active region length is 10 x 10-4 cm. The natural frequency of oscillation is
Options- A. 1 MHz
- B. 10 MHz
- C. 1 GHz
- D. 10 GHz Discuss
- 9. A cycloconverter is a group of controlled rectifiers.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. If the valence electron is separated from a copper atom, the remaining part of atom has a net charge of
Options- A. 1
- B. - 1
- C. 0
- D. + 3 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: T is kept constant and Ton is varied
Correct Answer: ± 30%
Correct Answer: increasing the power handling capacity
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: 1 a
Explanation:
First character must be alphabet.
Correct Answer: 0.2%
Explanation:
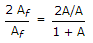
As we know, Gain with feedback
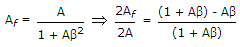
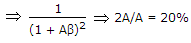
A = - 1000, ? = -0.1 .
Correct Answer: conductivity
Correct Answer: 10 GHz
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: 1
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
