Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics and Communication Engineering ‣ Analog Electronics See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
In figure v1 = 8 V and v2 = 8 V. Which diode will conduct?
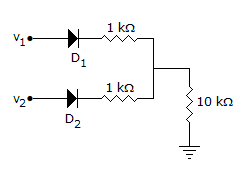
Options- A. D1 only
- B. D2 only
- C. Both D1 and D2
- D. Neither D1 nor D2
- Correct Answer
- Both D1 and D2
ExplanationBoth D1 and D2 are forward biased.
More questions
- 1. A particular green LED emits light of wavelength 5490, ┼, the energy bandgap of the semiconductor material used there is .. h = 6.6 x 10-34 J sec.
Options- A. 2.26 eV
- B. 1.98 eV
- C. 1.17 eV
- D. 0.74 eV Discuss
Correct Answer: 2.26 eV
Explanation:
From Plank equation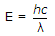 joule
joule
to convert it into electron volt it will be divided by 1.6 x 10-19.
- 2. As compared to a p-n junction diode
Options- A. a schottky diode has lower cut in voltage and lower reverse saturation current
- B. a schottky diode has higher cut in voltage and higher reverse saturation current
- C. a Schottky diode has lower cut in voltage and higher reverse saturation current
- D. a schottky diode has higher cut in voltage and lower reverse saturation current Discuss
Correct Answer: a Schottky diode has lower cut in voltage and higher reverse saturation current
- 3. From the noise point of view, bandwidth should
Options- A. be large
- B. not be too large
- C. should be as large as possible
- D. should be infinite Discuss
Correct Answer: not be too large
Explanation:
If noise is to be eliminated, bandwidth cannot be large.- 4. In a 4 bit weighted resistor D/A converter, the resistor value corresponding to LSB is 32 k?. The resistor value corresponding to MSB will be
Options- A. 32 K?
- B. 16 K?
- C. 8 K?
- D. 4 K? Discuss
Correct Answer: 4 K?
Explanation:
2n - 1 R = 32 K&Omeg;n = 4
? 8R = 32
R = 4 K?.
- 5. The word enhancement mode is associated with
Options- A. tunnel diode
- B. MOSFET
- C. JFET
- D. photo diode Discuss
Correct Answer: MOSFET
Explanation:
MOSFET may be depletion mode or enhancement mode.- 6. When a current source I is suddenly connected across a two terminal relaxed RC circuit at time t = 0, the voltage across the current source is shown in figure. The RC circuit is
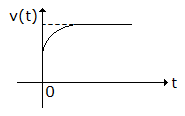
Options- A. a series combination of R and C
- B. a parallel combination of R and C
- C. a series combination of R and parallel combination of R and C
- D. a pure capacitor Discuss
Correct Answer: a series combination of R and parallel combination of R and C
Explanation:
Initially capacitor behaves as short-circuit and finally as open circuit.- 7. In a computer the instructions, data, intermediate and final results during processing are held in ALU.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: False
Explanation:
These are not held in ALU. Only computations are done by ALU.- 8. Which of the following is correct for a BJT?
Options- A.
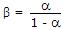
- B.
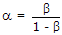
- C.
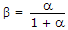
- D.
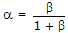 Discuss
Discuss
Correct Answer: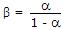
- 9. Radiation intensity of a dipole depends strongly on frequency. If at a frequency f, the intensity of radiation is 'I'. Then at a frequency of f/2, the intensity will be
Options- A.
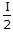
- B.
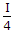
- C.
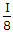
- D.
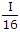 Discuss
Discuss
Correct Answer: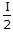
Explanation:
I ? f.- 10. A series RL circuit has
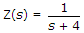 . If a voltage 4 sint + 4t is applied, the steady state current will be
. If a voltage 4 sint + 4t is applied, the steady state current will be
Options- A. 4 sin (4t - 45░)
- B.
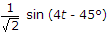
- C.
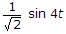
- D.
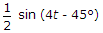 Discuss
Discuss
Correct Answer: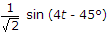
Explanation:
R = 4 ?, L = 1 H, ? = 4 rad/sec, XL = 4 ?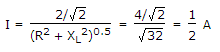
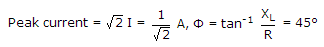
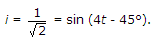
Comments
There are no comments.
More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ęCuriousTab. All rights reserved.
