Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ Advanced Surveying See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The correction applied to the measured base of length L is
Options- A.
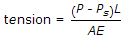
- B.
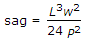 where w is the weight of tape/m
where w is the weight of tape/m - C.
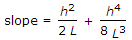 where h is height difference of end supports
where h is height difference of end supports - D. Reduction to mean sea level =
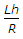
- E. all the above.
- Correct Answer
- all the above.
- 1. The self-cleansing velocity of water flowing through pipe lines, is
Options- A. 2 metres/sec
- B. 1 metre/sec
- C. 0.5 metre/sec
- D. 0.25 metre/sec. Discuss
- 2. The semi-infinite snow albedo is proportional to the square root of the grain radius :
Options- A. in the 0.2 to 0.4 ?m wave length region
- B. in the 0.4 to 0.8 ?m wave length region
- C. in the 0.8 to 1.2 ?m wave length
- D. None of these Discuss
- 3. To avoid the tendency of separation of liquid flow, the most suitable ratio of the diameters of the throat and the pipe, is
Options- A. 1/4 to 1/8
- B. 1/3 to 1/2
- C. 1/2 to 3/4.
- D. none of these. Discuss
- 4. The efficiency of a pump may be taken as
Options- A. 0.55
- B. 0.60
- C. 0.65
- D. 0.70 Discuss
- 5. A wooden block fixed on back side of a door frame on its post, is known as
Options- A. cleat
- B. stop
- C. horn
- D. none of these. Discuss
- 6. If a 30 m chain diverges through a perpendicular distance d from its correct alignment, the error in length, is
Options- A.
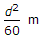
- B.

- C.
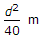
- D.
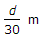
- E.
 .
Discuss
.
Discuss
- 7. In sewers the highest non-scouring velocity is achieved in
Options- A. glazed bricks sewers
- B. cast iron sewers
- C. cement concrete sewers
- D. stone ware sewers. Discuss
- 8. The difference in gradients after full super-elevation and the initial alignment of a road, is known as
Options- A. ruling gradient
- B. rising gradient
- C. compensated gradient
- D. differential gradient
- E. none of these. Discuss
- 9. The radius of influence is
Options- A. radius of the main well
- B. distance from the wall of main well to the point of zero draw down
- C. distance from the centre of main well to the point of zero draw down
- D. none of these. Discuss
- 10. The initial setting time of lime-pozzolana, is
Options- A. 30 minutes
- B. 60 minutes
- C. 90 minutes
- D. 120 minutes. Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 2 metres/sec
Correct Answer: in the 0.4 to 0.8 ?m wave length region
Correct Answer: 1/3 to 1/2
Correct Answer: 0.65
Correct Answer: stop
Correct Answer:
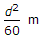
Correct Answer: glazed bricks sewers
Correct Answer: differential gradient
Correct Answer: distance from the centre of main well to the point of zero draw down
Correct Answer: 120 minutes.
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
