Discussion
Home ‣ Civil Engineering ‣ RCC Structures Design See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
For M 150 mix concrete, according to I.S. specifications, local bond stress, is
Options- A. 5 kg/cm2
- B. 10 kg/cm2
- C. 15 kg/cm2
- D. 20 kg/cm2
- E. 25 kg/cm2
- Correct Answer
- 10 kg/cm2
- 1. Pick up the in-correct statement from the following :
Options- A. Apparent solar time is measured from the lower transit of the true sun
- B. Mean solar time is measured from the lower transit of the mean sun
- C. Sidereal time is measured from the lower transit of the first point of Aries
- D. Sidereal time is measured from the upper transit of the first point of Aries. Discuss
- 2. To orient a plane table at a point P roughly south of the mid-point of two inaccessible conical hill stations A and B in the plains, a point C is selected in line with AB and table is oriented at C by bringing ab in line with AB. A ray is then drawn towards P and at P the table is oriented by back ray method. The orientation so obtained, is
Options- A. unique and correct
- B. incorrect
- C. manifold and correct
- D. not reliable. Discuss
- 3. The deflection of any rectangular beam simply supported, is
Options- A. directly proportional to its weight
- B. inversely proportional to its width
- C. inversely proportional to the cube of its depth
- D. directly proportional to the cube of its length
- E. none of these. Discuss
- 4. A simply supported beam (l + 2a) with equal overhangs (a) carries a uniformly distributed load over the whole length, the B.M. changes sign if
Options- A. l > 2a
- B. l < 2a
- C. l = 2a
- D. l = 4a
- E. l = 3a. Discuss
- 5. Shrouding is provided in
Options- A. cavity type tube wells
- B. slotted type tube wells
- C. strainer type tube wells
- D. perforated type tube wells. Discuss
- 6. Pick up the correct statement from the following :
Options- A. the sun's right ascension increases for 0 h to 24 h when it returns to the First point of Aries
- B. the maximum declination of the sun increases up to 23
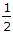 ° N on about 21st June
° N on about 21st June - C. the minimum declination of the sun is zero' on 22nd September
- D. the maximum declination of the sun is about 23
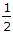 ° S on 21st December
° S on 21st December - E. all the above. Discuss
- 7. For high flood estimates the average value of the constant C in Dicken's formula Q = CA3/4, is
Options- A. 6.5
- B. 8.5
- C. 9.5
- D. 10.5
- E. 11.5 Discuss
- 8. Power can be expressed as
Options- A. work/energy
- B. work/time
- C. work x time
- D. work/distance. Discuss
- 9. The method of reversal
Options- A. is usually directed to examine whether a certain part is truly parallel or perpendicular to another
- B. makes the erroneous relationship between parts evident
- C. both (a) and (b)
- D. neither (a) nor (b). Discuss
- 10. Pick up the correct statement from the following:
Options- A. For steel castings, the minimum tensile strength is 41 kg/mm2 and minimum yield stress is 20.5 kg/mm2
- B. For mild steel the minimum tensile strength is 44 kg/mm2 and minimum elongation of 23% on a gauge length of 5.65A
- C. For high tensile steel, the minimum tensile strength is 58 kg/mm2
- D. All the above. Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: Sidereal time is measured from the upper transit of the first point of Aries.
Correct Answer: manifold and correct
Correct Answer: inversely proportional to the cube of its depth
Correct Answer: l > 2a
Correct Answer: slotted type tube wells
Correct Answer: all the above.
Correct Answer: 11.5
Correct Answer: work/time
Correct Answer: both (a) and (b)
Correct Answer: All the above.
Comments
There are no comments.More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
